Blockage of Galectin-Receptor Interactions Attenuates Mouse Hepatic Pathology Induced by Toxoplasma gondii Infection
- PMID: 35911679
- PMCID: PMC9327616
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.896744
Blockage of Galectin-Receptor Interactions Attenuates Mouse Hepatic Pathology Induced by Toxoplasma gondii Infection
Abstract
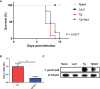
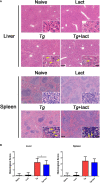
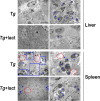
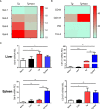
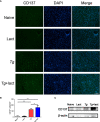
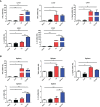
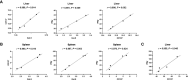
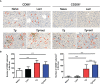
Toxoplasma gondii (T. gondii), one of the most important Apicomplexan protozoa, causes toxoplasmosis in human throughout the world. Galectin (Gal)-9 triggers a series of immune events via binding to its receptors, including T cell immunoglobulin and mucin-containing molecule 3, CD137, CD44, and protein disulfide isomerase. To examine the regulatory role of galectin-receptor interactions in anti-toxoplasmic activities, C57BL/6 mice were infected with T. gondii RH strain and intraperitoneally injected with alpha (α)-lactose to block the interactions of galectins and their receptors. Heatmaps showed upregulated values for Gal-9 and CD137 in the livers of T. gondii-infected mice and T. gondii-infected mice treated with α-lactose. Compared with T. gondii-infected mice, T. gondii-infected mice treated with α-lactose showed significantly increased survival rate, decreased tissue parasite burden, attenuated liver histopathology, increased mRNA expression levels of CD137, IFNγ, IL-4, and IL-10 in the liver, and increased Gal-9 mRNA expression level in the spleen. Correlation analysis showed that significant positive correlations existed between the mRNA expression levels of Gal-9 and CD137, Gal-9 and IFNγ, as well as between CD137 and IFNγ in the liver and spleen of T. gondii-infected mice; between CD137 and IFNγ in the liver of T. gondii-infected mice treated with α-lactose. In addition, blockage of galectin-receptor interactions showed enhanced M2 macrophage polarization in the liver of T. gondii-infected mice. Our data indicate that Gal-9-CD137 interaction may play an important role in T. gondii proliferation and liver inflammation in mice during acute T. gondii infection, through regulating T cell and macrophage immune responses.
Keywords: C57BL/6 mice; CD137; Gal-9; T. gondii; hepatic pathology.
Copyright © 2022 He, Hou and Lu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Galectin-receptor interaction: a key player in liver fibrosis induced by Schistosoma japonicum infection.Parasit Vectors. 2024 May 20;17(1):232. doi: 10.1186/s13071-024-06314-5. Parasit Vectors. 2024. PMID: 38769548 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Galectin-Receptor Interactions on Liver Pathology During the Erythrocytic Stage of Plasmodium berghei Malaria.Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 24;12:758052. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.758052. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34899708 Free PMC article.
-
Galectin-3 and Galectin-9 May Differently Regulate the Expressions of Microglial M1/M2 Markers and T Helper 1/Th2 Cytokines in the Brains of Genetically Susceptible C57BL/6 and Resistant BALB/c Mice Following Peroral Infection With Toxoplasma gondii.Front Immunol. 2018 Jul 31;9:1648. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01648. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30108583 Free PMC article.
-
[Toxoplasma gondii: a potential role in the genesis of psychiatric disorders].Encephale. 2013 Feb;39(1):38-43. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2012.06.014. Epub 2012 Aug 21. Encephale. 2013. PMID: 23095600 Review. French.
-
The Role of microRNAs in the Infection by T. gondii in Humans.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 May 14;11:670548. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.670548. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34055667 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Galectin-receptor interaction: a key player in liver fibrosis induced by Schistosoma japonicum infection.Parasit Vectors. 2024 May 20;17(1):232. doi: 10.1186/s13071-024-06314-5. Parasit Vectors. 2024. PMID: 38769548 Free PMC article.
-
CAR-NKT Cells in Asthma: Use of NKT as a Promising Cell for CAR Therapy.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2024 Jun;66(3):328-362. doi: 10.1007/s12016-024-08998-0. Epub 2024 Jul 12. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38995478 Review.
References
-
- Reid AJ, Vermont SJ, Cotton JA, Harris D, Hill-Cawthorne GA, Konen-Waisman S, et al. . Comparative Genomics of the Apicomplexan Parasites Toxoplasma Gondii and Neospora Caninum: Coccidia Differing in Host Range and Transmission Strategy. PLoS Pathog (2012) 8(3):22. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002567 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Doğan N, Kabukçuoğlu S, Vardareli E. Toxoplasmic Hepatitis in an Immunocompetent Patient. Turkiye Parazitol Derg (2007) 31(4):260–3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

