Two Step Selection for Bias in β Chain V-J Pairing
- PMID: 35911711
- PMCID: PMC9330483
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.906217
Two Step Selection for Bias in β Chain V-J Pairing
Abstract
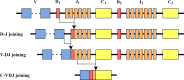
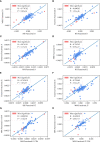
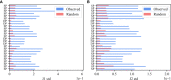
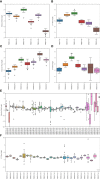
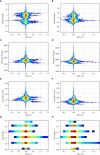
The β chain rearrangement in T cells is a two-step process where first Dβ and Jβ bind, and only then Vβ is joined to the complex. We here show that the frequency of human and mouse Vβ Jβ combinations deviates from the one expected based on each gene usage frequency. This bias is observed mainly in functional (F) rearrangements, but also slightly in non-functional (NF) rearrangements. Preferred Vβ Jβ combinations in F clones are shared between donors and samples, suggesting a common structural mechanism for these biases in addition to any host-specific antigen-induced peripheral selection. The sharing holds even in clones with J β 1 that share the same Dβ 1 gene. Vβ Jβ usage is correlated with the Molecular Weight and Isoelectric Point in F clones. The pairing is also observed in the Double Positive cells in mice thymocytes, suggesting that the selection leading to such a pairing occurs before thymic selection. These results suggest an additional structural checkpoint in the beta chain development prior to thymic selection during the T cell receptor expression. Understanding this structural selection is important for the distinction between normal and aberrant T cell development, and crucial for the design of engineered TCRs.
Keywords: TCR beta chain CDR3 repertoire; TCR repertoire; V-D-J rearrangement; junction length; selection.
Copyright © 2022 Levi and Louzoun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. t:
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of the expressed porcine Vbeta and Jbeta repertoire of thymocytes and peripheral T cells.Immunology. 2005 Feb;114(2):184-93. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2004.02072.x. Immunology. 2005. PMID: 15667563 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms that direct ordered assembly of T cell receptor beta locus V, D, and J gene segments.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Jul 5;97(14):7975-80. doi: 10.1073/pnas.130190597. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 10869424 Free PMC article.
-
Non-productive human TCR beta chain genes represent V-D-J diversity before selection upon function: insight into biased usage of TCRBD and TCRBJ genes and diversity of CDR3 region length.Hum Immunol. 1999 Nov;60(11):1090-100. doi: 10.1016/s0198-8859(99)00099-3. Hum Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10600007
-
High Incidence of Clonal CD8+ T-cell Proliferation in Non-malignant Conditions May Reduce the Significance of T-cell Clonality Assay for Differential Diagnosis in Oncohematology.Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020 Apr;20(4):203-208. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2019.12.021. Epub 2020 Jan 8. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020. PMID: 32046930 Review.
-
Regulation of T-cell receptor beta-chain gene assembly by recombination signals: the beyond 12/23 restriction.Immunol Rev. 2004 Aug;200:36-43. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2004.00156.x. Immunol Rev. 2004. PMID: 15242394 Review.
Cited by
-
Shared bias in H chain V-J pairing in naive and memory B cells.Front Immunol. 2023 Sep 18;14:1166116. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1166116. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37790930 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

