Drosophila Innate Immunity Involves Multiple Signaling Pathways and Coordinated Communication Between Different Tissues
- PMID: 35911716
- PMCID: PMC9336466
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.905370
Drosophila Innate Immunity Involves Multiple Signaling Pathways and Coordinated Communication Between Different Tissues
Abstract
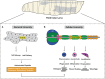
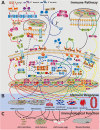
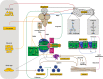
The innate immune response provides the first line of defense against invading pathogens, and immune disorders cause a variety of diseases. The fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster employs multiple innate immune reactions to resist infection. First, epithelial tissues function as physical barriers to prevent pathogen invasion. In addition, macrophage-like plasmatocytes eliminate intruders through phagocytosis, and lamellocytes encapsulate large particles, such as wasp eggs, that cannot be phagocytosed. Regarding humoral immune responses, the fat body, equivalent to the mammalian liver, secretes antimicrobial peptides into hemolymph, killing bacteria and fungi. Drosophila has been shown to be a powerful in vivo model for studying the mechanism of innate immunity and host-pathogen interactions because Drosophila and higher organisms share conserved signaling pathways and factors. Moreover, the ease with which Drosophila genetic and physiological characteristics can be manipulated prevents interference by adaptive immunity. In this review, we discuss the signaling pathways activated in Drosophila innate immunity, namely, the Toll, Imd, JNK, JAK/STAT pathways, and other factors, as well as relevant regulatory networks. We also review the mechanisms by which different tissues, including hemocytes, the fat body, the lymph gland, muscles, the gut and the brain coordinate innate immune responses. Furthermore, the latest studies in this field are outlined in this review. In summary, understanding the mechanism underlying innate immunity orchestration in Drosophila will help us better study human innate immunity-related diseases.
Keywords: Drosophila; immune response; innate immunity; signaling pathway; tissue communication.
Copyright © 2022 Yu, Luo, Xu, Zhang and Jin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tissue communication in a systemic immune response of Drosophila.Fly (Austin). 2016 Jul 2;10(3):115-22. doi: 10.1080/19336934.2016.1182269. Epub 2016 Apr 26. Fly (Austin). 2016. PMID: 27116253 Free PMC article.
-
The host defense of Drosophila melanogaster.Annu Rev Immunol. 2007;25:697-743. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.25.022106.141615. Annu Rev Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17201680 Review.
-
Drosophila phagocytosis - still many unknowns under the surface.APMIS. 2011 Oct;119(10):651-62. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0463.2011.02792.x. Epub 2011 Jul 21. APMIS. 2011. PMID: 21917002 Review.
-
Ubiquitin signalling in Drosophila innate immune responses.FEBS J. 2024 Oct;291(20):4397-4413. doi: 10.1111/febs.17028. Epub 2023 Dec 18. FEBS J. 2024. PMID: 38069549 Review.
-
The Drosophila lymph gland is an ideal model for studying hematopoiesis.Dev Comp Immunol. 2018 Jun;83:60-69. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2017.11.017. Epub 2017 Nov 27. Dev Comp Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29191551 Review.
Cited by
-
Drosophila melanogaster larvae are tolerant to oral infection with the bacterial pathogen Photorhabdus luminescens.MicroPubl Biol. 2023 Aug 29;2023:10.17912/micropub.biology.000938. doi: 10.17912/micropub.biology.000938. eCollection 2023. MicroPubl Biol. 2023. PMID: 37711508 Free PMC article.
-
Cul2 Is Essential for the Drosophila IMD Signaling-Mediated Antimicrobial Immune Defense.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 14;26(6):2627. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062627. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141268 Free PMC article.
-
JAK/STAT mediated insulin resistance in muscles is essential for effective immune response.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Apr 2;22(1):203. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01575-0. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38566182 Free PMC article.
-
Heterorhabditis bacteriophora Extracellular Vesicles Alter the Innate Immune Signaling in Drosophila melanogaster.Genes (Basel). 2025 May 22;16(6):613. doi: 10.3390/genes16060613. Genes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40565505 Free PMC article.
-
A U3 snoRNA is required for the regulation of chromatin dynamics and antiviral response in Drosophila melanogaster.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Jul 19;53(14):gkaf715. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf715. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 40737091 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

