Effects of Metabolism on Macrophage Polarization Under Different Disease Backgrounds
- PMID: 35911719
- PMCID: PMC9331907
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.880286
Effects of Metabolism on Macrophage Polarization Under Different Disease Backgrounds
Abstract
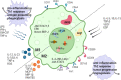
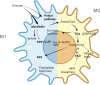
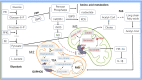
Macrophages are versatile immune cells associated with various diseases, and their phenotypes and functions change on the basis of the surrounding environments. Reprogramming of metabolism is required for the proper polarization of macrophages. This review will focus on basic metabolic pathways, the effects of key enzymes and specific products, relationships between cellular metabolism and macrophage polarization in different diseases and the potential prospect of therapy targeted key metabolic enzymes. In particular, the types and characteristics of macrophages at the maternal-fetal interface and their effects on a successful conception will be discussed.
Keywords: macrophage; maternal-fetal interface; metabolism; polarization; pregnancy.
Copyright © 2022 Sun, Xu and Jin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

