Acinar Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicle MiRNA-183-5p Aggravates Acute Pancreatitis by Promoting M1 Macrophage Polarization Through Downregulation of FoxO1
- PMID: 35911777
- PMCID: PMC9326086
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.869207
Acinar Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicle MiRNA-183-5p Aggravates Acute Pancreatitis by Promoting M1 Macrophage Polarization Through Downregulation of FoxO1
Abstract
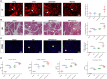
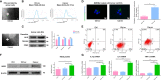
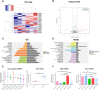
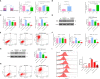
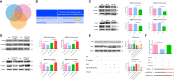
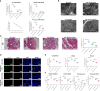
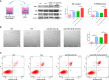
Acute pancreatitis (AP) is a common cause of a clinically acute abdomen. Crosstalk between acinar cells and leukocytes (especially macrophages) plays an important role in the development of AP. However, the mechanism mediating the interaction between acinar cells and macrophages is still unclear. This study was performed to explore the role of acinar cell extracellular vesicles (EVs) in the crosstalk between acinar cells and macrophages involved in the pathogenesis of AP. EVs derived from caerulein-treated acinar cells induced macrophage infiltration and aggravated pancreatitis in an AP rat model. Further research showed that acinar cell-derived EV miR-183-5p led to M1 macrophage polarization by downregulating forkhead box protein O1 (FoxO1), and a dual-luciferase reporter assay confirmed that FoxO1 was directly inhibited by miR-183-5p. In addition, acinar cell-derived EV miR-183-5p reduced macrophage phagocytosis. Acinar cell-derived EV miR-183-5p promoted the pancreatic infiltration of M1 macrophages and increased local and systemic damage in vivo. Subsequently, miR-183-5p overexpression in macrophages induced acinar cell damage and trypsin activation, thus further exacerbating the disease. In clinical samples, elevated miR-183-5p levels were detected in serum EVs and positively correlated with the severity of AP. EV miR-183-5p might play an important role in the development of AP by facilitating M1 macrophage polarization, providing a new insight into the diagnosis and targeted management of pancreatitis. Graphical abstract of the present study. In our caerulein-induced AP model, miR-183-5p was upregulated in injured acinar cells and transported by EVs to macrophages. miR-183-5p could induce M1 macrophage polarization through downregulation of FoxO1 and the release of inflammatory cytokines, which could aggravate AP-related injuries. Therefore, a vicious cycle might exist between injured ACs and M1 macrophage polarization, which is fulfilled by EV-transported miR-183-5p, leading to sustainable and progressive AP-related injuries.
Keywords: acute pancreatitis; exosome; extracellular vesicles; inflammation; macrophage polarization.
Copyright © 2022 Tang, Cao, Yan, Cui, Guo, Cheng, Li, Li, Ma, Fang, Gao, Ren, Sun, Wang and Ji.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MALAT1 shuttled by extracellular vesicles promotes M1 polarization of macrophages to induce acute pancreatitis via miR-181a-5p/HMGB1 axis.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Oct;25(19):9241-9254. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16844. Epub 2021 Aug 27. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34448533 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes Derived From Cerulein-Stimulated Pancreatic Acinar Cells Mediate Peritoneal Macrophage M1 Polarization and Pyroptosis via an miR-24-3p/MARCH3/NLRP3 Axis in Acute Pancreatitis.Pancreas. 2024 Sep 1;53(8):e641-e651. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000002351. Epub 2024 Mar 27. Pancreas. 2024. PMID: 38530976
-
Extracellular vesicles derived from M1 macrophages deliver miR-146a-5p and miR-146b-5p to suppress trophoblast migration and invasion by targeting TRAF6 in recurrent spontaneous abortion.Theranostics. 2021 Mar 31;11(12):5813-5830. doi: 10.7150/thno.58731. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33897883 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of M1 Macrophages and Their Extracellular Vesicles in Cancer Therapy.Cells. 2024 Aug 26;13(17):1428. doi: 10.3390/cells13171428. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39273000 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fighting Fire with Fire: Exosomes and Acute Pancreatitis-Associated Acute Lung Injury.Bioengineering (Basel). 2022 Oct 26;9(11):615. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering9110615. Bioengineering (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36354526 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ulinastatin inhibits macrophage M1 polarization to improve acute pancreatitis-associated intestinal barrier dysfunction by promoting Nrf2 signaling pathway activation.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Jul 26;30(1):676. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02952-2. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40713698 Free PMC article.
-
Pancreatic Crosstalk in the Disease Setting: Understanding the Impact of Exocrine Disease on Endocrine Function.Compr Physiol. 2024 Mar 29;14(2):5371-5387. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c230008. Compr Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39109973 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasma Exosomes Aggravate Acute Pancreatitis by Promoting M1 Polarization of Adipose Tissue Macrophages in Obesity-Related Severe Acute Pancreatitis.Dig Dis Sci. 2023 Sep;68(9):3660-3670. doi: 10.1007/s10620-023-08021-0. Epub 2023 Jul 15. Dig Dis Sci. 2023. PMID: 37452979
-
The Pivotal Role of Macrophages in the Pathogenesis of Pancreatic Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 25;25(11):5765. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115765. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38891952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of MicroRNAs in Pancreatitis Development and Progression.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 5;24(2):1057. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021057. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36674571 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

