Recurrence of LV Thrombus in a Patient with Severe Ischaemic Cardiomyopathy Anticoagulated with Apixaban
- PMID: 35911864
- PMCID: PMC9334074
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/8156942
Recurrence of LV Thrombus in a Patient with Severe Ischaemic Cardiomyopathy Anticoagulated with Apixaban
Abstract
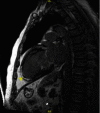
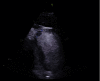
Background: Anticoagulation with warfarin remains the mainstay treatment for left ventricular thrombi. Although successful thrombus resolution has been reported with direct oral anticoagulants' (DOACs') recurrence/progression while resuming Apixaban therapy is yet to be reported. Case Presentation. This case report describes left ventricular thrombus progression/recurrence in a patient anticoagulated with Apixaban undergoing implantable cardioverter defibrillator to cardiac resynchronisation therapy with defibrillator upgrade procedure. He was thereafter changed to warfarin. Contrast echocardiogram at 6 months follow-up did not identify the previously demonstrated mural thrombus.
Conclusion: Prospective randomised control trials should be conducted in patients with left ventricular thrombus to compare anticoagulants, assess the efficacy and safety of DOACs, and evaluate uninterrupted DOAC versus transient withdrawal for cardiac device procedures.
Copyright © 2022 Azhar Farooqui et al.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Garber A. M., Mentz R. J., Al-khalidi H., Shaw L. K., Fiuzat M., O'connor C. Clinical predictors and outcomes of patients with left ventricular thrombus following ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Journal of Thrombosis and Thrombolysis . 2016;41(3):365–373. doi: 10.1007/s11239-015-1252-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Crawford T. C., Smith W. T., IV, Velazquez E. J., Taylor S. M., Jollis J. G., Kisslo J. Prognostic usefulness of left ventricular thrombus by echocardiography in dilated cardiomyopathy in predicting stroke, transient ischemic attack, and death. American Chemical Journal . 2004;93(4):500–503. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2003.10.056. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

