A Study Regarding Nursing Leadership
- PMID: 35911948
- PMCID: PMC9289596
- DOI: 10.12865/CHSJ.48.01.17
A Study Regarding Nursing Leadership
Abstract
Purpose: The research included the analysis and processing of questionnaires applied in county hospitals in Craiova. The purpose of this article is to highlight the qualities, skills and competencies of a leader, necessary in the development of leadership and professional development skills.
Material and method: We performed a descriptive and cross-sectional study involving 166 medical staff from hospitals in Craiova. Between January 2020 and January 2021, we used a questionnaire as an investigative tool containing 26 questions on complex leadership issues. The results were stored in Microsoft Excel files (Microsoft Corp., Redmond, WA, USA) and were statistically analyzed using the Microsoft Excel XLST AT (Addinsoft) software suite. SARL, Paris,). Secondary data processing: calculation of fundamental statistical parameters, mean and standard deviation of their ratio, coefficient of variation, graphical representation and calculation of regression coefficients was performed with Excel, Pivot Tables using controls, Functions, Statistics, Diagram and Data Analysis module. In conclusion, a better organization of the management of the hospital units is required, taking into account the leadership in nursing.
Keywords: Interpersonal relationships; leadership; management; nurse’s roles; professional problems.
Copyright © 2014, Medical University Publishing House Craiova.
Conflict of interest statement
None to declare.
Figures
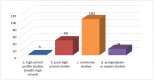



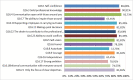

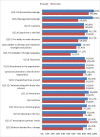

References
-
- Stanley D, Stanley K. Clinical leadership and nursing explored: A literature search. J Clin Nurs. 2018;27(9-10):1730–1743. - PubMed
-
- Salvage J, White J. Nursing leadership and health policy: everybody’s business. Int Nurs Rev. 2019;66(2):147–150. - PubMed
-
- Zhu Z, Xing W, Liang Y, Hong L, Hu Y. Nursing students' experiences with service learning: A qualitative systematic review and meta-synthesis. Nurse Educ Today. 2022;108:105206–105206. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
