Chinese Herbal Medicine for Functional Dyspepsia With Psychological Disorders: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 35911981
- PMCID: PMC9330302
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2022.933290
Chinese Herbal Medicine for Functional Dyspepsia With Psychological Disorders: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background and aims: Functional dyspepsia (FD) is closely associated with gut-brain interaction disorder (DGBI), characterized by the interaction of gastrointestinal symptoms and central nervous system dysregulation. Chinese herbal medicine (CHM) has a good concurrent effect in the treatment of FD, especially for patients with concurrent psychological disorders. A meta-analysis was designed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of CHMs in the treatment of FD.
Methods: The PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, Chinese Biological Medical Database (CBM), Wanfang Data, China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), and China Science and Technology Journal Database (VIP) were searched to collect randomized controlled trials of FD treated with CHM. The retrieval time limit is from the establishment of the database till 11 April 2022. Two researchers independently searched databases, screened documents, extracted data, and evaluated the risk of bias of included studies. RevMan 5.4 software was used for meta-analysis.
Results: A total of 11 studies including 951 patients were included. The study was divided into two parts. The first part included 5 clinical trials, including 471 patients. The experimental group was treated only with CHM and the control group was only treated with placebo. The results of first part showed that the total effective rate of CHM in the treatment of FD was higher than that in the placebo group (84.5 vs. 49.4%) [relative risk (RR) = 1.76; 95% confidence interval (CI) (1.13, 2.75); P = 0.01]. In addition, CHM treatment could reduce the total symptom score [standardized mean difference (SMD) = -10.05; 95% CI (-13.50, -6.59); Z = 5.70; P < 0.0001] and depression score [SMD = -7.68; 95% CI (-14.43, -0.94); Z = 2.23; P = 0.03]. The second part included 6 clinical trials, including 480 patients. The experimental group was only treated with CHM and the control group was treated with prokinetic agents combined with flupentixol melitracen (deanxit). The results of second part showed that the total effective rate of CHM in the treatment of FD was higher than that of the control group (92.6 vs. 78.8%) [RR = 1.17; 95% CI (1.09, 1.26), P < 0.0001]. In addition, CHM treatment could reduce HAMA score [mean difference (MD) = -3.19; 95% CI (-3.79, -2.59); Z = 10.40; P < 0.00001], HAMD score [MD = -4.32; 95% CI (-6.04, -2.61); Z = 4.94; P < 0.00001], and gastric emptying rate [MD = 12.62; 95% CI (5.84, 19.40); Z = 3.65; P = 0.0003]. The results of the two parts of the meta-analysis showed no serious adverse reactions, and there was no significant difference in the adverse reactions between the experimental group and the control group [MD = 1.14; 95% CI (0.53, 2.42); Z = 0.33; P = 0.74]; [MD = 0.14; 95% CI (0.01, 2.67); Z = 1.30; P = 0.19].
Conclusion: The current evidence shows that CHM treatment has great potential and safety in alleviating the symptoms of FD and improving the psychological disorders of anxiety and depression in patients with FD. Limited by the quantity and quality of the included studies and other biases, the above conclusions need more high-quality studies to be verified.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/, identifier [CRD42022311129].
Keywords: Chinese herbal medicine; effectiveness; functional dyspepsia (FD); metaanalysis; psychological disorder.
Copyright © 2022 Luo, Wang, Fang, Qing, Jiang, Yang, Su and Wei.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





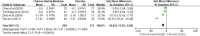

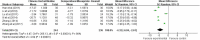




References
-
- Chen G., Feng P., Wang S., Ding X., Xiong J., Wu J., et al. (2020). An Herbal Formulation of Jiawei Xiaoyao for the Treatment of Functional Dyspepsia: A Multicenter, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Clinical Trial. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 11:e00241. 10.14309/ctg.0000000000000241 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen Y. L. (2016). The psychosomatics viewpoint of chronic gastrointestinal disease. Chin. J. Diagn. Electron. 4 168–172.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

