Role and mechanism of miR-211 in human cancer
- PMID: 35912006
- PMCID: PMC9330454
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.71401
Role and mechanism of miR-211 in human cancer
Abstract
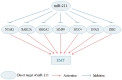
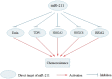
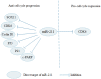
MircoRNA (miRNA), which are a group of small, and highly conserved non-coding RNA consisting of 18-25 nucleotides, can modulate gene expression at post-transcriptional level, through complementary binding to the 3'-untranslated region (3'-UTR) of numerous target genes. Emerging evidence indicates that miRNAs play critical roles in tumorigenesis and progression of cancer. Among them, miR-211 has been extensively studied in multiple cancers. The expression of miR-211 significantly varies with cancer types and may be used as a potential prognostic marker for cancer. MiR-211 can regulate multiple biological processes in cancer, including proliferation, apoptosis, metastasis and drug resistance. Additionally, several factors may contribute to the dysregulation of miR-211 in cancer. Consequently, this review aims to discuss the novel findings that highlight latent value of miR-211 in the prognosis assessment and treatment of cancer.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interaction of microRNAs with sphingosine kinases, sphingosine-1 phosphate, and sphingosine-1 phosphate receptors in cancer.Discov Oncol. 2021 Sep 20;12(1):33. doi: 10.1007/s12672-021-00430-9. Discov Oncol. 2021. PMID: 35201458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MiR-145 in cancer therapy resistance and sensitivity: A comprehensive review.Cancer Sci. 2020 Sep;111(9):3122-3131. doi: 10.1111/cas.14517. Epub 2020 Jul 8. Cancer Sci. 2020. PMID: 32506767 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MiR-145: a potential biomarker of cancer migration and invasion.Am J Transl Res. 2019 Nov 15;11(11):6739-6753. eCollection 2019. Am J Transl Res. 2019. PMID: 31814885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging roles of MiR-133a in human cancers.J Cancer. 2021 Jan 1;12(1):198-206. doi: 10.7150/jca.48769. eCollection 2021. J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33391416 Free PMC article.
-
miR-190-5p in human diseases.Cancer Cell Int. 2019 Oct 7;19:257. doi: 10.1186/s12935-019-0984-x. eCollection 2019. Cancer Cell Int. 2019. PMID: 31624470 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanistic and therapeutic perspectives of non-coding RNA-modulated apoptotic signaling in diabetic retinopathy.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024 Jul 6;40(1):53. doi: 10.1007/s10565-024-09896-z. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38970639 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New insights of miRNA molecular mechanisms in breast cancer brain metastasis and therapeutic targets.Noncoding RNA Res. 2023 Sep 28;8(4):645-660. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2023.09.003. eCollection 2023 Dec. Noncoding RNA Res. 2023. PMID: 37818447 Free PMC article.
-
The Multifaceted Role of miR-211 in Health and Disease.Biomolecules. 2025 Aug 1;15(8):1109. doi: 10.3390/biom15081109. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40867554 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unveiling Epigenetic Regulatory Elements Associated with Breast Cancer Development.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 8;26(14):6558. doi: 10.3390/ijms26146558. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40724805 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging roles of non-coding RNAs in modulating the PI3K/Akt pathway in cancer.Noncoding RNA Res. 2024 Aug 9;10:1-15. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2024.08.002. eCollection 2025 Feb. Noncoding RNA Res. 2024. PMID: 39296640 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

