Lumbar-peritoneal shunt for idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus and secondary normal pressure hydrocephalus
- PMID: 35912046
- PMCID: PMC9333098
- DOI: 10.4103/tcmj.tcmj_125_21
Lumbar-peritoneal shunt for idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus and secondary normal pressure hydrocephalus
Abstract
Objectives: Normal-pressure hydrocephalus is a clinical syndrome consisting of dilated cerebral ventricles with the clinical triad of gait disturbance, cognitive impairment and/or urinary dysfunction. Lumbar-peritoneal (LP) shunt could improve idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (iNPH) while its effectiveness on secondary NPH (sNPH) is elusive. We compared the clinical results of the patients who received LP shunt surgery between iNPH and sNPH.
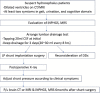
Materials and methods: We retrospectively analyzed the patients who received LP shunt surgery in a single center from January 1, 2017, to June 30, 2017. Patients selected for LP shunt placement had at least two of three cardinal symptoms of iNPH. The symptoms should persist for more than 3 months with compatible brain magnetic resonance imaging findings. All patients were followed up with iNPH grading scale (iNPHGS) and Modified Rankin Scale (MRS) for evaluation.
Results: Thirty-three patients (23 male and 10 female patients) with mean age 76-year-old completed follow-up in this study, and 17 patients received lumbar drainage tests and intracranial pressure measurements. Both iNPH (n = 22) and sNPH (n = 11) groups did not have major complications such as infection, nerve root injury, or shunt failure. Both groups have significant improvement in iNPHGS and MRS. Interestingly, we found the correlation between both opening intracranial pressure and pressure gradient difference to the improvement percentage from LP shunt.
Conclusion: The safety and effectiveness for sNPH patients who received LP shunt placement are equivalent to the iNPH patients. Lumbar drainage test provides prerequisite outcome prediction and should be considered to identify NPH patients planned to receive LP shunt.
Keywords: Lumbar-peritoneal shunt; Normal pressure hydrocephalus; Outcome.
Copyright: © 2021 Tzu Chi Medical Journal.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Shinn-Zong Lin, an editorial board member at Tzu Chi Medical Journal, had no role in the peer review process of or decision to publish this article. The other authors declared no conflicts of interest in writing this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Disability risk or unimproved symptoms following shunt surgery in patients with idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus: post hoc analysis of SINPHONI-2.J Neurosurg. 2017 Jun;126(6):2002-2009. doi: 10.3171/2016.5.JNS16377. Epub 2016 Jul 15. J Neurosurg. 2017. PMID: 27419822
-
Revisiting secondary normal pressure hydrocephalus: does it exist? A review.Neurosurg Focus. 2016 Sep;41(3):E6. doi: 10.3171/2016.6.FOCUS16189. Neurosurg Focus. 2016. PMID: 27581318 Review.
-
One-year outcome in patients with idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus: comparison of lumboperitoneal shunt to ventriculoperitoneal shunt.J Neurosurg. 2016 Dec;125(6):1483-1492. doi: 10.3171/2015.10.JNS151894. Epub 2016 Feb 12. J Neurosurg. 2016. PMID: 26871203
-
Utility of MRI-based disproportionately enlarged subarachnoid space hydrocephalus scoring for predicting prognosis after surgery for idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: clinical research.J Neurosurg. 2017 Dec;127(6):1436-1442. doi: 10.3171/2016.9.JNS161080. Epub 2017 Feb 3. J Neurosurg. 2017. PMID: 28156249
-
Diagnosis and Treatment of Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus.Continuum (Minneap Minn). 2016 Apr;22(2 Dementia):579-99. doi: 10.1212/CON.0000000000000305. Continuum (Minneap Minn). 2016. PMID: 27042909 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Secondary normal pressure hydrocephalus following pituitary apoplexy: A case report.Surg Neurol Int. 2024 Mar 22;15:100. doi: 10.25259/SNI_32_2024. eCollection 2024. Surg Neurol Int. 2024. PMID: 38628523 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pal SS, Dubey S. A study of VP shunt in management of hydrocephalus. Int Surg J. 2017;4:1697–701.
-
- Krahulik D, Vaverka M, Hrabalek L, Hampl M, Halaj M, Jablonsky J, et al. Ventriculoperitoneal shunt in treating of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus-single-center study. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2020;162:1–7. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
