Cerebral endothelial cell derived small extracellular vesicles improve cognitive function in aged diabetic rats
- PMID: 35912073
- PMCID: PMC9330338
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.926485
Cerebral endothelial cell derived small extracellular vesicles improve cognitive function in aged diabetic rats
Abstract
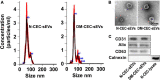
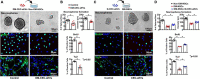
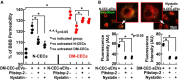
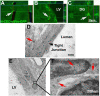
Small extracellular vesicles (sEVs) mediate cell-cell communication by transferring their cargo biological materials into recipient cells. Diabetes mellitus (DM) induces cerebral vascular dysfunction and neurogenesis impairment, which are associated with cognitive decline and an increased risk of developing dementia. Whether the sEVs are involved in DM-induced cerebral vascular disease, is unknown. Therefore, we studied sEVs derived from cerebral endothelial cells (CEC-sEVs) of aged DM rats (DM-CEC-sEVs) and found that DM-CEC-sEVs robustly inhibited neural stem cell (NSC) generation of new neuroblasts and damaged cerebral endothelial function. Treatment of aged DM-rats with CEC-sEVs derived from adult healthy normal rats (N-CEC-sEVs) ameliorated cognitive deficits and improved cerebral vascular function and enhanced neurogenesis. Intravenously administered N-CEC-sEVs crossed the blood brain barrier and were internalized by neural stem cells in the neurogenic region, which were associated with augmentation of miR-1 and -146a and reduction of myeloid differentiation primary response gene 88 and thrombospondin 1 proteins. In addition, uptake of N-CEC-sEVs by the recipient cells was mediated by clathrin and caveolin dependent endocytosis signaling pathways. The present study provides ex vivo and in vivo evidence that DM-CEC-sEVs induce cerebral vascular dysfunction and neurogenesis impairment and that N-CEC-sEVs have a therapeutic effect on improvement of cognitive function by ameliorating dysfunction of cerebral vessels and increasing neurogenesis in aged DM rats, respectively.
Keywords: cerebral endothelial cell; cognitive function; diabete mellitus; exosomes; neural stem cells; rat; small extracellular vesicles.
Copyright © 2022 Zhang, Li, Huang, Teng, Zhang, Zhou, Liu, Fan, Luo, He, Zhao, Lu, Chopp and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Small extracellular vesicles secreted by induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve postoperative cognitive dysfunction in mice with diabetes.Neural Regen Res. 2023 Mar;18(3):609-617. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.350205. Neural Regen Res. 2023. PMID: 36018185 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebral endothelial cell-derived small extracellular vesicles enhance neurovascular function and neurological recovery in rat acute ischemic stroke models of mechanical thrombectomy and embolic stroke treatment with tPA.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2021 Aug;41(8):2090-2104. doi: 10.1177/0271678X21992980. Epub 2021 Feb 8. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2021. PMID: 33557693 Free PMC article.
-
Small extracellular vesicles derived from cerebral endothelial cells with elevated microRNA 27a promote ischemic stroke recovery.Neural Regen Res. 2025 Jan 1;20(1):224-233. doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-22-01292. Epub 2024 Mar 1. Neural Regen Res. 2025. PMID: 38767487 Free PMC article.
-
Neural stem cell-derived small extracellular vesicles: a new therapy approach in neurological diseases.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 16;16:1548206. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1548206. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40308614 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Noncoding RNAs from tissue-derived small extracellular vesicles: Roles in diabetes and diabetic complications.Mol Metab. 2022 Apr;58:101453. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2022.101453. Epub 2022 Feb 2. Mol Metab. 2022. PMID: 35121168 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Small Extracellular Vesicles From Hypoxia-Neuron Maintain Blood-Brain Barrier Integrity.Stroke. 2025 Jun;56(6):1569-1580. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.124.048446. Epub 2025 Apr 2. Stroke. 2025. PMID: 40171669 Free PMC article.
-
A perspective from the National Eye Institute Extracellular Vesicle Workshop: Gaps, needs, and opportunities for studies of extracellular vesicles in vision research.J Extracell Vesicles. 2024 Dec;13(12):e70023. doi: 10.1002/jev2.70023. J Extracell Vesicles. 2024. PMID: 39665315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles and Potential Mechanisms of Endothelial Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Ischemic Stroke.Transl Stroke Res. 2025 Oct;16(5):1836-1849. doi: 10.1007/s12975-025-01334-4. Epub 2025 Feb 7. Transl Stroke Res. 2025. PMID: 39918683 Review.
-
Mechanisms of extracellular vesicle uptake and implications for the design of cancer therapeutics.J Extracell Biol. 2024 Oct 30;3(11):e70017. doi: 10.1002/jex2.70017. eCollection 2024 Nov. J Extracell Biol. 2024. PMID: 39483807 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advanced Delivery Strategies for Immunotherapy in Type I Diabetes Mellitus.BioDrugs. 2023 May;37(3):331-352. doi: 10.1007/s40259-023-00594-6. Epub 2023 May 13. BioDrugs. 2023. PMID: 37178431 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

