A Radiomics Nomogram Integrated With Clinic-Radiological Features for Preoperative Prediction of DNA Mismatch Repair Deficiency in Gastric Adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 35912185
- PMCID: PMC9327646
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.865548
A Radiomics Nomogram Integrated With Clinic-Radiological Features for Preoperative Prediction of DNA Mismatch Repair Deficiency in Gastric Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Purpose: To develop and validate a radiomics nomogram integrated with clinic-radiological features for preoperative prediction of DNA mismatch repair deficiency (dMMR) in gastric adenocarcinoma.
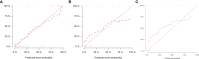
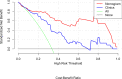
Materials and methods: From March 2014 to August 2020, 161 patients with pathologically confirmed gastric adenocarcinoma were included from two centers (center 1 as the training and internal testing sets, n = 101; center 2 as the external testing sets, n = 60). All patients underwent preoperative contrast-enhanced computerized tomography (CT) examination. Radiomics features were extracted from portal-venous phase CT images. Max-relevance and min-redundancy (mRMR) and least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) methods were used to select features, and then radiomics signature was constructed using logistic regression analysis. A radiomics nomogram was built incorporating the radiomics signature and independent clinical predictors. The model performance was assessed using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis, calibration curve, and decision curve analysis (DCA).
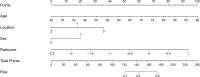
Results: The radiomics signature, which was constructed using two selected features, was significantly associated with dMMR gastric adenocarcinoma in the training and internal testing sets (P < 0.05). The radiomics signature model showed a moderate discrimination ability with an area under the ROC curve (AUC) of 0.81 in the training set, which was confirmed with an AUC of 0.78 in the internal testing set. The radiomics nomogram consisting of the radiomics signature and clinical factors (age, sex, and location) showed excellent discrimination in the training, internal testing, and external testing sets with AUCs of 0.93, 0.82, and 0.83, respectively. Further, calibration curves and DCA analysis demonstrated good fit and clinical utility of the radiomics nomogram.
Conclusions: The radiomics nomogram combining radiomics signature and clinical characteristics (age, sex, and location) may be used to individually predict dMMR of gastric adenocarcinoma.
Keywords: DNA mismatch repair deficiency; X-ray computed; gastric cancer/adenocarcinoma; nomogram; radiomics; tomography.
Copyright © 2022 Tong, Li, Chen, Hu, Xu, Duan, Wang, Yu and Cheng.
Conflict of interest statement
Author SD was employed by GE Healthcare. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Peltomäki P, Lothe RA, Aaltonen LA, Pylkkänen L, Nyström-Lahti M, Seruca R, et al. . Microsatellite Instability Is Associated With Tumors That Characterize the Hereditary Non-Polyposis Colorectal Carcinoma Syndrome. Cancer Res (1993) 53(24):5853–5. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19931215)72:12 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

