Glaucocalyxin A Inhibits the Malignant Progression of Epithelial Ovarian Cancer by Affecting the MicroRNA-374b-5p/HMGB3/Wnt-β-Catenin Pathway Axis
- PMID: 35912216
- PMCID: PMC9329791
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.955830
Glaucocalyxin A Inhibits the Malignant Progression of Epithelial Ovarian Cancer by Affecting the MicroRNA-374b-5p/HMGB3/Wnt-β-Catenin Pathway Axis
Abstract
Objective: Glaucocalyxin A (GLA) is an ent-kaurene diterpenoid from Rabdosia japonica var possessing anti-tumor activity. This study aimed to investigate effects of GLA on epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) and elucidate underlying mechanisms.
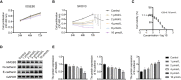
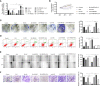
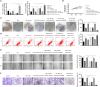
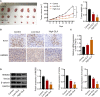
Methods: The expression of HMGB3 in EOC tissues was analyzed by GEPIA and immunohistochemistry. Cell proliferation was determined using CCK-8 and colony formation assays. Cell invasion, migration, and apoptosis were detected using Transwell, wound healing, and flow cytometry assays, respectively. Interactions between HMGB3 and miRNAs were predicted using ENCORI and validated using a dual-luciferase assay. mRNA expression levels of HMGB3 and miRNAs were measured using qPCR. Protein expression levels of HMGB3, E-cadherin, N-cadherin, Wnt3a,β-catenin, Bcl-2, and Bax were measured by western blotting. A tumor xenograft model was established to validate the efficacy and mechanism of GLA in vivo.
Results: HMGB3 was upregulated in EOC tissues and cells. GLA dose-dependently inhibited EOC cell proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). HMGB3 overexpression promoted proliferation, invasion, migration, and EMT, and suppressed the apoptosis of EOC cells. In addition, miR-374b-5p was targeted by HMGB3, and its overexpression hindered malignant characteristics of EOC cells. HMGB3 overexpression weakened antitumor effects of GLA and miR-374b-5p in EOC cells. Moreover, the Wnt-β-catenin pathway was inhibited by the GLA-mediated miR-374b-5p/HMGB3 axis. In vivo experiments showed that GLA inhibited EOC tumor growth, meanwhile, upregulated the miR-374b-5p level and downregulated the expression of HMGB3, Wnt3a, and β-catenin in tumor tissues.
Conclusions: GLA suppressed the malignant progression of EOC by regulating the miR-374b-5p/HMGB3/Wnt-β-catenin pathway axis.
Keywords: Wnt-β-catenin pathway; epithelial ovarian cancer; glaucocalyxin A; high-mobility group box 3; microRNA-374b-5p.
Copyright © 2022 Chen, Sun, Liu, Shao and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Long Noncoding RNA SOX2-OT Knockdown Inhibits Proliferation and Metastasis of Prostate Cancer Cells Through Modulating the miR-452-5p/HMGB3 Axis and Inactivating Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway.Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2020 Nov;35(9):682-695. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2019.3479. Epub 2020 May 14. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2020. PMID: 32407168
-
Circ_CLIP2 promotes glioma progression through targeting the miR-195-5p/HMGB3 axis.J Neurooncol. 2021 Sep;154(2):131-144. doi: 10.1007/s11060-021-03814-7. Epub 2021 Aug 6. J Neurooncol. 2021. PMID: 34357490
-
Downregulation of microRNA-532-5p promotes the proliferation and invasion of bladder cancer cells through promotion of HMGB3/Wnt/β-catenin signaling.Chem Biol Interact. 2019 Feb 25;300:73-81. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2019.01.015. Epub 2019 Jan 11. Chem Biol Interact. 2019. PMID: 30639441
-
Long non-coding RNA NORAD contributes to the proliferation, invasion and EMT progression of prostate cancer via the miR-30a-5p/RAB11A/WNT/β-catenin pathway.Cancer Cell Int. 2020 Nov 27;20(1):571. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-01665-2. Cancer Cell Int. 2020. PMID: 33292272 Free PMC article.
-
The role of high mobility group protein B3 (HMGB3) in tumor proliferation and drug resistance.Mol Cell Biochem. 2021 Apr;476(4):1729-1739. doi: 10.1007/s11010-020-04015-y. Epub 2021 Jan 11. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33428061 Review.
Cited by
-
Downregulation of ITIH3 contributes to cisplatin-based chemotherapy resistance in ovarian carcinoma via the Bcl-2 mediated anti-apoptosis signaling pathway.Oncol Lett. 2022 Dec 21;25(2):61. doi: 10.3892/ol.2022.13646. eCollection 2023 Feb. Oncol Lett. 2022. PMID: 36644154 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

