ZFAND5 Is an Independent Prognostic Biomarker of Perihilar Cholangiocarcinoma
- PMID: 35912230
- PMCID: PMC9326020
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.955670
ZFAND5 Is an Independent Prognostic Biomarker of Perihilar Cholangiocarcinoma
Abstract
Background: Cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) is a highly aggressive malignancy with extremely poor prognosis. Perihilar CCA (pCCA) is the most common subtype of CCA, but its biomarker study is much more lagged behind other subtypes. ZFAND5 protein can interact with ubiquitinated proteins and promote protein degradation. However, the function of ZFAND5 in cancer progression is rarely investigated, and the role of ZFAND5 in pCCA is never yielded.
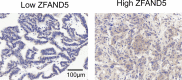
Materials and methods: In this study, we established a pCCA cohort consisting of 72 patients. The expression of ZFAND5 in pCCAs, and the paired liver tissues, intrahepatic bile duct tissues and common bile ducts (CBD) tissues were detected with IHC. ZFAND5 mRNA in pCCAs and CBDs was detected with qRT-PCR. The pCCA cohort was divided into ZFAND5low and ZFAND5high subsets according to the IHC score. The correlations between ZFAND5 expression and clinicopathological parameters were assessed bychi-square test. The prognostic significance of ZFAND5 expression and clinicopathological parameters was estimated by univariate analysis with Kaplan-Meier method, and by multivariate analysis with Cox-regression model.
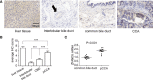
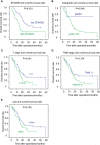
Results: Expression of ZFAND5 in pCCAs was substantially higher than that in interlobular bile ducts and common bile ducts, but lower than that in liver tissues. The ZFAND5low and ZFAND5high subsets accounted for 44.4% and 55.6% of all pCCAs respectively. ZFAND5 high patients had much lower survival rates than the ZFAND5low patients, with the average survival time as 31.2 months and 19.5 months respectively. ZFAND5 was identified as an independent unfavorable prognostic biomarker of pCCA with multivariate analysis.
Conclusion: ZFAND5 expression was up-regulated in pCCAs compared with the CBDs. We identified ZFAND5 as an independent biomarker of pCCA, which could provide more evidence for the molecular classification of pCCA, and help stratify the high-risk patients based on the molecular features.
Keywords: ZFAND5; biomarker; cohort; perihilar cholangiocarcinoma; prognosis.
Copyright © 2022 Liu, Wang and Duan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dual-Specificity Phosphatase 11 Is a Prognostic Biomarker of Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma.Front Oncol. 2021 Sep 29;11:757498. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.757498. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34660327 Free PMC article.
-
The expression, clinical relevance, and prognostic significance of HJURP in cholangiocarcinoma.Front Oncol. 2022 Jul 28;12:972550. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.972550. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35965590 Free PMC article.
-
The Smad4-MYO18A-PP1A complex regulates β-catenin phosphorylation and pemigatinib resistance by inhibiting PAK1 in cholangiocarcinoma.Cell Death Differ. 2022 Apr;29(4):818-831. doi: 10.1038/s41418-021-00897-7. Epub 2021 Nov 19. Cell Death Differ. 2022. PMID: 34799729 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted Therapies for Perihilar Cholangiocarcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Mar 31;14(7):1789. doi: 10.3390/cancers14071789. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35406560 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current Perspectives on the Surgical Management of Perihilar Cholangiocarcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Apr 28;14(9):2208. doi: 10.3390/cancers14092208. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35565335 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CircPMS1 promotes proliferation of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells, pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells, and pericytes under hypoxia.Animal Model Exp Med. 2024 Jun;7(3):310-323. doi: 10.1002/ame2.12332. Epub 2023 Jun 14. Animal Model Exp Med. 2024. PMID: 37317637 Free PMC article.
-
ARID1A silencing-mediated upregulation of microRNA-652 accelerates cigarette smoke-induced human bronchial epithelial cell transformation by targeting ZFAND5.BMC Pulm Med. 2025 May 20;25(1):245. doi: 10.1186/s12890-025-03718-6. BMC Pulm Med. 2025. PMID: 40394521 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

