Pathogens and Pathogenesis in Wheezing Diseases in Children Under 6
- PMID: 35912246
- PMCID: PMC9329614
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.922214
Pathogens and Pathogenesis in Wheezing Diseases in Children Under 6
Abstract
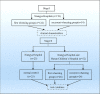
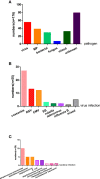
Few studies have comprehensively assessed the roles of cytokine production in wheezing pathogenesis. Therefore, we undertook this study to determine the association between wheezing episodes and cytokines, and to provide further information on this topic. Firstly, we retrospectively collected I176 children, including 122 subjects with first wheezing and 54 subjects with recurrent wheezing, to analyze the etiology and clinical characteristics of children with wheezing diseases. Then, we collected 52 children with wheezing diseases and 25 normal controls to detect the expression of interferon-γ (IFN-γ), interleukin-4 (IL-4), IFN-γ/IL-4, IL-17A, IL-17E, IgE, matrix metalloproteinase-3 (MMP-3), and MMP-9 in serum or plasma. The results showed that boys under 3 years old with history of allergies were more likely to develop wheezing diseases. In our cohort, M. pneumoniae caused a greater proportion of wheezing in children than expected. The expression of IgE [18.80 (13.65-31.00) vs. 17.9 (10.15-21.60)], IL-4 [24.00 (24.00-48.00) vs. 23.00 (9.50-27.00)], IFN-γ [70.59 (41.63-116.46) vs. 49.83 (29.58-81.74)], MMP3 [53.40 (20.02-128.2) vs. 30.90 (13.80-50.95)], MMP9 [148.10 (99.30-276.10) vs. 122.10 (82.20-162.35)], IL-17A [80.55 (54.46-113.08) vs. 61.11 (29.43-93.87)], and IL-17E [1.75 (0.66-2.77) vs. 1.19 (0.488-2.1615)] were significantly increased in the wheezing group (p<0.05) compared to normal controls, while the level of IFN-γ/IL-4 had no significant difference between the two groups (1.24 ± 1.88 vs 0.68 ± 0.74, p>0.05). There was altered cytokine production in children with wheezing diseases which was quite similar to asthma pathogenesis. Sex, age, pathogen infection, and inflammation in our study were also risk factors for wheezing diseases.
Keywords: IFN-γ; IL-17; IL-4; IgE; MMP; infant; wheezing.
Copyright © 2022 Tang, Yang, He, Huang, Zheng and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Increased production of IFN-gamma and cysteinyl leukotrienes in virus-induced wheezing.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999 Apr;103(4):630-6. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(99)70235-6. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10200012
-
Longitudinal plasma cytokine concentrations and recurrent wheezing after RSV bronchiolitis.Cytokine. 2021 Apr;140:155434. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2021.155434. Epub 2021 Jan 26. Cytokine. 2021. PMID: 33513527
-
Bidirectional interactions between viral respiratory illnesses and cytokine responses in the first year of life.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006 Jan;117(1):72-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2005.10.002. Epub 2005 Nov 28. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16387587
-
[Viral infection and asthma: immunologic mechanisms].Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2001 May-Jun;29(3):126-33. doi: 10.1016/s0301-0546(01)79032-5. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2001. PMID: 11434887 Review. Spanish.
-
[The role of infection in asthma].Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2001 May-Jun;29(3):147-51. doi: 10.1016/s0301-0546(01)79035-0. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2001. PMID: 11434890 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Guardian's knowledge and attitude towards inhaled corticosteroids aerosol therapy and medication compliance of children with wheezing diseases.Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2024 Jul 24;20(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s13223-024-00908-5. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39049039 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

