Radiomic Signatures for Predicting EGFR Mutation Status in Lung Cancer Brain Metastases
- PMID: 35912248
- PMCID: PMC9334014
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.931812
Radiomic Signatures for Predicting EGFR Mutation Status in Lung Cancer Brain Metastases
Abstract
Background: Lung cancer is the most common primary tumor metastasizing to the brain. A significant proportion of lung cancer patients show epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation status discordance between the primary cancer and the corresponding brain metastases, which can affect prognosis and therapeutic decision-making. However, it is not always feasible to obtain brain metastases samples. The aim of this study was to establish a radiomic model to predict the EGFR mutation status of lung cancer brain metastases.
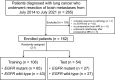
Methods: Data from 162 patients with resected brain metastases originating from lung cancer (70 with mutant EGFR, 92 with wild-type EGFR) were retrospectively analyzed. Radiomic features were extracted using preoperative brain magnetic resonance (MR) images (contrast-enhanced T1-weighted imaging, T1CE; T2-weighted imaging, T2WI; T2 fluid-attenuated inversion recovery, T2 FLAIR; and combinations of these sequences), to establish machine learning-based models for predicting the EGFR status of excised brain metastases (108 metastases for training and 54 metastases for testing). The least absolute shrinkage selection operator was used to select informative features; radiomics models were built with logistic regression of the training cohort, and model performance was evaluated using an independent test set.
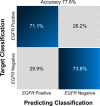
Results: The best-performing model was a combination of 10 features selected from multiple sequences (two from T1CE, five from T2WI, and three from T2 FLAIR) in both the training and test sets, resulting in classification area under the curve, accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity values of 0.85 and 0.81, 77.8% and 75.9%, 83.7% and 73.1%, and 73.8% and 78.6%, respectively.
Conclusions: Radiomic signatures integrating multi-sequence MR images have the potential to noninvasively predict the EGFR mutation status of lung cancer brain metastases.
Keywords: brain neoplasms; epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR); lung cancer; magnetic resonance imaging; radiomics.
Copyright © 2022 Zheng, Xie, Luo, Yang, Zhang, Li, Yin, Li and Xie.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Radiomics signature of brain metastasis: prediction of EGFR mutation status.Eur Radiol. 2021 Jul;31(7):4538-4547. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07614-x. Epub 2021 Jan 13. Eur Radiol. 2021. PMID: 33439315
-
Radiomic Signatures for Predicting Receptor Status in Breast Cancer Brain Metastases.Front Oncol. 2022 Jun 6;12:878388. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.878388. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35734585 Free PMC article.
-
Diffusion tensor and postcontrast T1-weighted imaging radiomics to differentiate the epidermal growth factor receptor mutation status of brain metastases from non-small cell lung cancer.Neuroradiology. 2021 Mar;63(3):343-352. doi: 10.1007/s00234-020-02529-2. Epub 2020 Aug 21. Neuroradiology. 2021. PMID: 32827069
-
MR-based radiomics predictive modelling of EGFR mutation and HER2 overexpression in metastatic brain adenocarcinoma: a two-centre study.Cancer Imaging. 2024 May 21;24(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s40644-024-00709-4. Cancer Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38773634 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic accuracy of MRI-based radiomic features for EGFR mutation status in non-small cell lung cancer patients with brain metastases: a meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2025 Jan 6;14:1428929. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1428929. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39834943 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Current status and prospect of PET-related imaging radiomics in lung cancer.Front Oncol. 2023 Dec 18;13:1297674. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1297674. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38164195 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Bayesian meta-analysis on MRI-based radiomics for predicting EGFR mutation in brain metastasis of lung cancer.BMC Med Imaging. 2025 Feb 10;25(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s12880-025-01566-8. BMC Med Imaging. 2025. PMID: 39930347 Free PMC article.
-
The potential of MRI radiomics based on extrapulmonary metastases in predicting EGFR mutations: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Biomed Eng Online. 2025 Jan 17;24(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s12938-025-01331-6. Biomed Eng Online. 2025. PMID: 39825348 Free PMC article.
-
Radiomics for the non-invasive prediction of PD-L1 expression in patients with brain metastases secondary to non-small cell lung cancer.J Neurooncol. 2023 Jul;163(3):597-605. doi: 10.1007/s11060-023-04367-7. Epub 2023 Jun 29. J Neurooncol. 2023. PMID: 37382806 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning in prediction of epidermal growth factor receptor status in non-small cell lung cancer brain metastases: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2025 May 1;25(1):818. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14221-w. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40312289 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kris MG, Natale RB, Herbst RS, Lynch TJ, Prager D, Belani CP, et al. . Efficacy of Gefitinib, an Inhibitor of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase, in Symptomatic Patients With Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer - A Randomized Trial. JAMA-Journal Am Med Assoc (2003) 290(16):2149–58. doi: 10.1001/jama.290.16.2149 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

