Increased MPO in Colorectal Cancer Is Associated With High Peripheral Neutrophil Counts and a Poor Prognosis: A TCGA With Propensity Score-Matched Analysis
- PMID: 35912260
- PMCID: PMC9331745
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.940706
Increased MPO in Colorectal Cancer Is Associated With High Peripheral Neutrophil Counts and a Poor Prognosis: A TCGA With Propensity Score-Matched Analysis
Abstract
Background: Myeloperoxidase (MPO) has been demonstrated to be a local mediator of inflammation in tissue damage in various inflammatory diseases. Given its controversial effect on colorectal cancer (CRC), there has been growing interest in investigating the role of this enzyme in CRC. The mechanism underlying MPO activity and CRC progression requires further clarification.
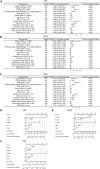
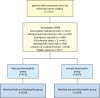
Methods: The expression and function of MPO in CRC were evaluated using TCGA analysis. TCGA, TIMER, and Human Cell Landscape analyses were used to analyze the correlation between MPO expression and neutrophil infiltration in CRC. Spearman's bivariate correlation analysis was used to verify the correlation between MPO levels in CRC and the peripheral neutrophil count. In the clinical analysis, 8,121 patients who underwent elective surgery for CRC were enrolled in this retrospective cohort study from January 2008 to December 2014. Propensity score matching was used to address the differences in baseline characteristics. The Kaplan-Meier method and Cox regression analysis were used to identify independent prognostic factors in patients with CRC.
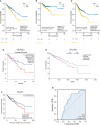
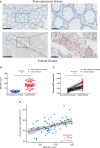
Results: MPO was upregulated in CRC tissues, which is related to malignant progression and worse survival in CRC patients from TCGA analysis. MPO was significantly correlated with the infiltration level of neutrophils in CRC in TCGA, TIMER, and Human Cell Landscape analyses. MPO was positively correlated with the peripheral neutrophil count. Data of the 8,121 patients who underwent CRC surgery were available for analysis. After propensity score matching, 3,358 patients were included in each group. Kaplan-Meier survival curves showed that high preoperative neutrophil levels were associated with decreased overall survival (OS; P < 0.001) and disease-free survival (DFS; P = 0.015). The preoperative neutrophil count was an independent risk factor for OS (hazard ratio [HR], 1.157; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.055-1.268; P = 0.002) and DFS (HR, 1.118; 95% CI, 1.009-1.238; P = 0.033).
Conclusions: Our research indicates that increased MPO levels in CRC are significantly correlated with high preoperative neutrophil counts, and both serve as prognostic indicators for worse survival in CRC patients. Our study suggests that neutrophils may be key players in the mechanism linking MPO levels with poor CRC outcomes.
Keywords: TCGA analysis; colorectal cancer; myeloperoxidase; preoperative neutrophil counts; prognosis; propensity score-matched analysis.
Copyright © 2022 Weng, Yue, Wu, Zhou, Guo, Sun, Liao, Sun, Zhou and Miao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Anemia tolerance versus blood transfusion on long-term outcomes after colorectal cancer surgery: A retrospective propensity-score-matched analysis.Front Oncol. 2022 Aug 15;12:940428. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.940428. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36046042 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophils to lymphocytes ratio as a useful prognosticator for stage II colorectal cancer patients.BMC Cancer. 2018 Dec 3;18(1):1202. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-5042-x. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30509242 Free PMC article.
-
High preoperative white blood cell count determines poor prognosis and is associated with an immunosuppressive microenvironment in colorectal cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Jul 29;12:943423. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.943423. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35965545 Free PMC article.
-
Higher Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR) Is a Preoperative Inflammation Biomarker of Poor Prognosis in HIV-Infected Patients with Colorectal Cancer: A Retrospective Study.Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023 Mar 6;2023:7966625. doi: 10.1155/2023/7966625. eCollection 2023. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 36923659 Free PMC article.
-
High Expression of MMP-9 in Primary Tumors and High Preoperative MPO in Serum Predict Improved Prognosis in Colorectal Cancer with Operable Liver Metastases.Oncology. 2021;99(3):144-160. doi: 10.1159/000510609. Epub 2020 Oct 7. Oncology. 2021. PMID: 33027796
Cited by
-
Proteomic Profiling Informs Mechanisms of Esophageal Adenocarcinoma Inhibition by Cranberry Proanthocyanidins.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2025 Aug;69(15):e70102. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.70102. Epub 2025 May 12. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2025. PMID: 40351102 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying molecular subtypes and tumor microenvironment infiltration signatures in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma based on stemness-associated disulfidptosis genes by integrating machine learning, single-cell analyses and experimental validation.Heliyon. 2024 Feb 13;10(4):e26094. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26094. eCollection 2024 Feb 29. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38390172 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative tissue proteome profile reveals neutrophil degranulation and remodeling of extracellular matrix proteins in early stage gallbladder cancer.Front Oncol. 2023 Jan 6;12:1046974. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1046974. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36686780 Free PMC article.
-
High serum proteinase-3 levels predict poor progression-free survival and lower efficacy of bevacizumab in metastatic colorectal cancer.BMC Cancer. 2024 Feb 2;24(1):165. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-11924-4. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38308214 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of resistance to bevacizumab plus FOLFOX in metastatic colorectal cancer-Results of the prospective multicenter PERMAD trial.PLoS One. 2024 Jun 14;19(6):e0304324. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0304324. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38875244 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

