Drug hypersensitivity, in vitro tools, biomarkers, and burden with COVID-19 vaccines
- PMID: 35912413
- PMCID: PMC9537799
- DOI: 10.1111/all.15461
Drug hypersensitivity, in vitro tools, biomarkers, and burden with COVID-19 vaccines
Abstract
Hypersensitivity reactions to drugs are increasing worldwide. They display a large degree of variability in the immunological mechanisms involved, which impacts both disease severity and the optimal diagnostic procedure. Therefore, drug hypersensitivity diagnosis relies on both in vitro and in vivo assessments, although most of the methods are not well standardized. Moreover, several biomarkers can be used as valuable parameters for precision medicine that provide information on the endotypes, diagnosis, prognosis, and prediction of drug hypersensitivity development, as well on the identification of therapeutic targets and treatment efficacy monitoring. Furthermore, in the last 2 years, the SARS-CoV-2 (severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus) pandemic has had an important impact on health system, leading us to update approaches on how to manage hypersensitivity reactions to drugs used for its treatment and on COVID-19 (Coronavirus disease) vaccines used for its prevention. This article reviews recent advances in these 3 areas regarding drug hypersensitivity: in vitro tools for drug hypersensitivity diagnosis, recently identified biomarkers that could guide clinical decision making and management of hypersensitivity reactions to drugs and vaccines used for COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; biomarkers; hypersensitivity reactions; in vitro test; vaccines.
© 2022 European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

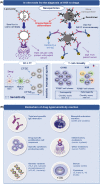

References
-
- Beyaz Ş, Akdeniz N, Yılmaz A, et al. Diagnostic workup including CD203c‐based basophil activation test in immediate hypersensitivity due to metronidazole and ornidazole and evaluation of cross‐reactivity in between. Allergy. 2021;76:842‐852. - PubMed
-
- Prieto A, Muñoz C, Bogas G, et al. Single‐dose prolonged drug provocation test, without previous skin testing, is safe for diagnosing children with mild non‐immediate reactions to beta‐lactams. Allergy. 2021;76:2544‐2554. - PubMed
-
- You J, Sun L, Zhao Q, et al. Dynamic cytokine profiles combined with enzyme‐linked immunospot assay are useful for immunologically confirming the dapsone hypersensitivity syndrome. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:814‐816. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

