The role of selected nutraceuticals in management of prediabetes and diabetes: An updated review of the literature
- PMID: 35912631
- PMCID: PMC9804244
- DOI: 10.1002/ptr.7564
The role of selected nutraceuticals in management of prediabetes and diabetes: An updated review of the literature
Abstract
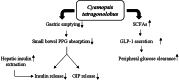
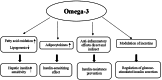
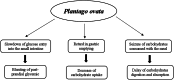
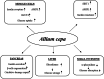
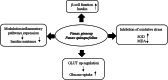
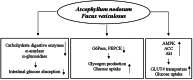
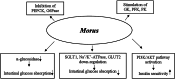
Dysglycemia is a disease state preceding the onset of diabetes and includes impaired fasting glycemia and impaired glucose tolerance. This review aimed to collect and analyze the literature reporting the results of clinical trials evaluating the effects of selected nutraceuticals on glycemia in humans. The results of the analyzed trials, generally, showed the positive effects of the nutraceuticals studied alone or in association with other supplements on fasting plasma glucose and post-prandial plasma glucose as primary outcomes, and their efficacy in improving insulin resistance as a secondary outcome. Some evidences, obtained from clinical trials, suggest a role for some nutraceuticals, and in particular Berberis, Banaba, Curcumin, and Guar gum, in the management of prediabetes and diabetes. However, contradictory results were found on the hypoglycemic effects of Morus, Ilex paraguariensis, Omega-3, Allium cepa, and Trigonella faenum graecum, whereby rigorous long-term clinical trials are needed to confirm these data. More studies are also needed for Eugenia jambolana, as well as for Ascophyllum nodosum and Fucus vesiculosus which glucose-lowering effects were observed when administered in combination, but not alone. Further trials are also needed for quercetin.
Keywords: IFG; IGT; dysglycemia; nutraceuticals; pre-diabetes.
© 2022 The Authors. Phytotherapy Research published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript. This includes employment, consultancies, honoraria, stock ownership or options, expert testimony, grants or patents received or pending, or royalties. No writing assistance was utilized in the production of this manuscript.
Figures







References
-
- Adab, Z. , Eghtesadi, S. , Vafa, M. R. , Heydari, I. , Shojaii, A. , Haqqani, H. , … Eghtesadi, M. (2019). Effect of turmeric on glycemic status, lipid profile, hs‐CRP, and total antioxidant capacity in hyperlipidemic type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Phytotherapy Research, 33(4), 1173–1181. - PubMed
-
- Aggarwal, B. B. , & Harikumar, K. B. (2009). Potential therapeutic effects of curcumin, the anti‐inflammatory agent, against neurodegenerative, cardiovascular, pulmonary, metabolic, autoimmune and neoplastic diseases. The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology, 41(1), 40–59. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

