Utilization of propranolol hydrochloride mucoadhesive invasomes as a locally acting contraceptive: in-vitro, ex-vivo, and in-vivo evaluation
- PMID: 35912869
- PMCID: PMC9347470
- DOI: 10.1080/10717544.2022.2100514
Utilization of propranolol hydrochloride mucoadhesive invasomes as a locally acting contraceptive: in-vitro, ex-vivo, and in-vivo evaluation
Abstract
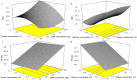
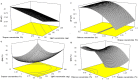
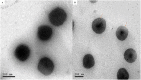
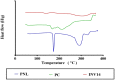
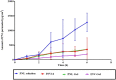
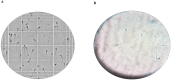
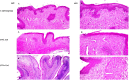
It was found that propranolol hydrochloride (PNL), which is a beta-blocker used for hypertension treatment, has a potent spermicidal activity through local anesthetic activity or beta-blocking effect on sperm cells subsequently it could be used as a contraceptive remedy. This study aimed to entrap PNL into invasomes (INVs) and then formulate it as a locally acting contraceptive gel. PNL-loaded mucoadhesive INVs were prepared via the thin-film hydration technique. The D-optimal design was utilized to fabricate INVs employing lipid concentration (X1), terpenes concentration (X2), terpenes type (X3), and chitosan concentration (X4) as independent variables, while their impact was observed for entrapment efficiency percent (Y1; EE%), particle size (Y2; PS), zeta potential (Y3; ZP), and amount of drug released after 6 h (Y4; Q6h). Design Expert® was bestowed to nominate the desired formula. The selected INV was subjected to further studies and formulated into a mucoadhesive gel for ex-vivo and in-vivo investigations. The optimum INV showed a spherical shape with EE% of 65.01 ± 1.24%, PS of 243.75 ± 8.13 nm, PDI of 0.203 ± 0.01, ZP of 49.80 ± 0.42 mV, and Q6h of 53.16 ± 0.73%. Differential scanning calorimetry study asserted the capability of INVs to entrap PNL. Permeation studies confirmed the desired sustained effect of PNL-loaded INVs-gel compared to PNL-gel, INVs, and PNL solution. Sperm motility assay proved the potency of INVs-gel to inhibit sperm motility. Besides, the histopathological investigation verified the tolerability of the prepared INVs-gel. Taken together, the gained data justified the efficacy of PNL-loaded INVs-gel as a potential locally acting contraceptive.
Keywords: Contraception; histopathological study; mucoadhesive invasomes; propranolol hydrochloride; spermicide; vaginal drug delivery.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chitosan decorated oleosomes loaded propranolol hydrochloride hydrogel repurposed for Candida albicans-vaginal infection.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2024 Jun 20;19(15):1369-1388. doi: 10.1080/17435889.2024.2359364. Epub 2024 Jun 20. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2024. PMID: 38900630 Free PMC article.
-
Nanocomposite alginate hydrogel loaded with propranolol hydrochloride kolliphor® based cerosomes as a repurposed platform for Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus-(MRSA)-induced skin infection; in-vitro, ex-vivo, in-silico, and in-vivo evaluation.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025 Feb;15(2):556-576. doi: 10.1007/s13346-024-01611-z. Epub 2024 May 18. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 38762697 Free PMC article.
-
Ultra-deformable liposomes containing terpenes (terpesomes) loaded fenticonazole nitrate for treatment of vaginal candidiasis: Box-Behnken design optimization, comparative ex vivo and in vivo studies.Drug Deliv. 2020 Dec;27(1):1514-1523. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2020.1837295. Drug Deliv. 2020. PMID: 33108907 Free PMC article.
-
Recent observations on drugs and human fertility.Postgrad Med J. 1988 Aug;64(754):578-80. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.64.754.578. Postgrad Med J. 1988. PMID: 3150539 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A comprehensive review on recent nanosystems for enhancing antifungal activity of fenticonazole nitrate from different routes of administration.Drug Deliv. 2023 Dec;30(1):2179129. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2023.2179129. Drug Deliv. 2023. PMID: 36788709 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lyophilized Nasal Inserts of Atomoxetine HCl Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Brain Targeting as a Treatment of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): A Pharmacokinetics Study on Rats.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Feb 20;16(2):326. doi: 10.3390/ph16020326. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37259468 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol-loaded invasome gel: A promising nanoformulation for treatment of skin cancer.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2024 Dec;14(12):3354-3370. doi: 10.1007/s13346-024-01534-9. Epub 2024 Feb 15. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 38361173 Free PMC article.
-
A poly-δ-decalactone (PDL) based nanoemulgel for topical delivery of ketoconazole and eugenol against Candida albicans.Nanoscale Adv. 2024 Aug 2;6(21):5322-36. doi: 10.1039/d4na00176a. Online ahead of print. Nanoscale Adv. 2024. PMID: 39247866 Free PMC article.
-
Unlocking the Power of Onion Peel Extracts: Antimicrobial and Anti-Inflammatory Effects Improve Wound Healing through Repressing Notch-1/NLRP3/Caspase-1 Signaling.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Sep 28;16(10):1379. doi: 10.3390/ph16101379. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37895850 Free PMC article.
-
Formulation and Evaluation of Prednisolone Sodium Metazoate-Loaded Mucoadhesive Quatsomal Gel for Local Treatment of Recurrent Aphthous Ulcers: Optimization, In Vitro, Ex Vivo, and In Vivo Studies.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jul 14;15(7):1947. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15071947. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37514134 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abd-Elsalam WH, El-Helaly SN, Ahmed MA, Al-mahallawi AM. (2018). Preparation of novel phospholipid-based sonocomplexes for improved intestinal permeability of rosuvastatin: in vitro characterization, dynamic simulation, Caco-2 cell line permeation and in vivo assessment studies. Int J Pharm 548:375–84. - PubMed
-
- Abdellatif MM, Khalil IA, Khalil MAF. (2017). Sertaconazole nitrate loaded nanovesicular systems for targeting skin fungal infection: in-vitro, ex-vivo and in-vivo evaluation. Int J Pharm 527:1–11. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
