Repressed Ang 1-7 in COVID-19 Is Inversely Associated with Inflammation and Coagulation
- PMID: 35913134
- PMCID: PMC9429950
- DOI: 10.1128/msphere.00220-22
Repressed Ang 1-7 in COVID-19 Is Inversely Associated with Inflammation and Coagulation
Abstract
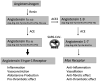
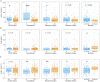
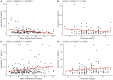
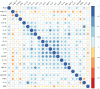
The coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 infects host cells by binding to the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor, which belongs to an anti-inflammatory, anti-thrombotic counter-regulatory arm of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS). ACE2 dysfunction and RAS dysregulation has been explored as a driving force in acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), but data from COVID-19 patients has been inconsistent and inconclusive. We sought to identify disruptions of the classical (ACE)/angiotensin (Ang) II/Ang II type-1 receptor (AT1R) and the counter-regulatory ACE2/Ang 1-7/Mas Receptor (MasR) pathways in patients with COVID-19 and correlate these with severity of infection and markers of inflammation and coagulation. Ang II and Ang 1-7 levels in plasma were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for 230 patients, 166 of whom were SARS-CoV-2+. Ang 1-7 was repressed in COVID-19 patients compared to that in SARS-CoV-2 negative outpatient controls. Since the control cohort was less sick than the SARS-CoV-2+ group, this association between decreased Ang 1-7 and COVID-19 cannot be attributed to COVID-19 specifically as opposed to critical illness more generally. Multivariable logistic regression analyses demonstrated that every 10-pg/mL increase in plasma Ang 1-7 was associated with a 3% reduction in the odds of hospitalization (adjusted odds ratio [AOR] 0.97, confidence interval [CI] 0.95 to 0.99) and a 3% reduction in odds of requiring oxygen supplementation (AOR 0.97, CI 0.95 to 0.99) and/or ventilation (AOR 0.97, CI 0.94 to 0.99). Ang 1-7 was also inversely associated with pro-inflammatory cytokines and d-dimer in this patient cohort, suggesting that reduced activity in this protective counter-regulatory arm of the RAS contributes to the hyper-immune response and diffuse coagulation activation documented in COVID-19. IMPORTANCE Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) causes a unique disease, COVID-19, which ranges in severity from asymptomatic to causing severe respiratory failure and death. Viral transmission throughout the world continues at a high rate despite the development and widespread use of effective vaccines. For those patients who contract COVID-19 and become severely ill, few therapeutic options have been shown to provide benefits and mortality rates are high. Additionally, the pathophysiology underlying COVID-19 disease presentation, progression, and severity is incompletely understood. The significance of our research is in confirming the role of renin-angiotensin system dysfunction in COVID-19 pathogenesis in a large cohort of patients with diverse disease severity and outcomes. Additionally, to our knowledge, this is the first study to pair angiotensin peptide levels with inflammatory and thrombotic markers. These data support the role of ongoing clinical trials examining renin-angiotensin system-targeted therapeutics for the treatment of COVID-19.
Keywords: Ang 1–7; COVID-19; coagulation; inflammation; renin-angiotensin system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Disequilibrium between the classic renin-angiotensin system and its opposing arm in SARS-CoV-2-related lung injury.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2020 Aug 1;319(2):L325-L336. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00189.2020. Epub 2020 Jul 8. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32639866 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ACE2 and COVID-19 and the resulting ARDS.Postgrad Med J. 2020 Jul;96(1137):403-407. doi: 10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-137935. Epub 2020 Jun 10. Postgrad Med J. 2020. PMID: 32522846 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Renin-Angiotensin System: An Important Player in the Pathogenesis of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 28;21(21):8038. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218038. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33126657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiotensin II Exaggerates SARS-CoV-2 Specific T-Cell Response in Convalescent Individuals following COVID-19.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 4;23(15):8669. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158669. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955801 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of ACE (Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme)-2 and Renin-Angiotensin Peptides in SARS-CoV-2 Mediated Mortality and End-Organ Injuries.Hypertension. 2022 Feb;79(2):365-378. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.121.18295. Epub 2021 Nov 30. Hypertension. 2022. PMID: 34844421
Cited by
-
Mechanisms of endothelial activation, hypercoagulation and thrombosis in COVID-19: a link with diabetes mellitus.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024 Feb 20;23(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-02097-8. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 38378550 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Timing matters in the use of renin-angiotensin system modulators and COVID-related cognitive and cerebrovascular dysfunction.PLoS One. 2024 Jul 29;19(7):e0304135. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0304135. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39074114 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of the pharmacokinetics of soluble ACE2 decoy receptors through glycosylation.Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2024 Jul 19;32(3):101301. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2024.101301. eCollection 2024 Sep 12. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2024. PMID: 39185275 Free PMC article.
-
Autoantibodies to ACE2 and immune molecules are associated with COVID-19 disease severity.Commun Med (Lond). 2024 Mar 15;4(1):47. doi: 10.1038/s43856-024-00477-z. Commun Med (Lond). 2024. PMID: 38491326 Free PMC article.
-
Myocardial Oedema as a Consequence of Viral Infection and Persistence-A Narrative Review with Focus on COVID-19 and Post COVID Sequelae.Viruses. 2024 Jan 14;16(1):121. doi: 10.3390/v16010121. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38257821 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization. 2021. Weekly Operational Update on COVID-19, 6 April 2021. https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update-on.... Accessed April 8, 2021.
-
- Gheblawi M, Wang K, Viveiros A, Nguyen Q, Zhong JC, Turner AJ, Raizada MK, Grant MB, Oudit GY. 2020. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: SARS-CoV-2 receptor and regulator of the renin-angiotensin system: celebrating the 20th anniversary of the discovery of ACE2. Circ Res 126:1456–1474. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317015. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

