Hibifolin, a Natural Sortase A Inhibitor, Attenuates the Pathogenicity of Staphylococcus aureus and Enhances the Antibacterial Activity of Cefotaxime
- PMID: 35913166
- PMCID: PMC9430695
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.00950-22
Hibifolin, a Natural Sortase A Inhibitor, Attenuates the Pathogenicity of Staphylococcus aureus and Enhances the Antibacterial Activity of Cefotaxime
Abstract
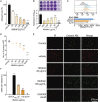
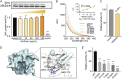
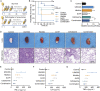
This study aimed to identify hibifolin as a sortase A (SrtA) inhibitor and to determine whether it could attenuate the virulence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). We employed a fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) assay to screen a library of natural molecules to identify compounds that inhibit SrtA activity. Fluorescence quenching assay and molecular docking were performed to verify the direct binding interaction between SrtA and hibifolin. The pneumonia model was established using C57BL/6J mice by MRAS nasal administration for evaluating the effect of hibifolin on the pathogenicity of MRSA. Herein, we found that hibifolin was able to inhibit SrtA activity with an IC50 of 31.20 μg/mL. Further assays showed that the capacity of adhesion of bacteria to the host cells and biofilm formation was decreased in hibifolin-treated USA300. Results obtained from fluorescence quenching assay and molecular docking indicated that hibifolin was capable of targeting SrtA protein directly. This interaction was further confirmed by the finding that the inhibition activities of hibifolin on mutant SrtA were substantially reduced after mutating the binding sites (TRP-194, ALA-104, THR-180, ARG-197, ASN-114). The in vivo study showed that hibifolin in combination with cefotaxime protected mice from USA300 infection-induced pneumonia, which was more potent than cefotaxime alone, and no significant cytotoxicity of hibifolin was observed. Taken together, we identified that hibifolin attenuated the pathogenicity of S. aureus by directly targeting SrtA, which may be utilized in the future as adjuvant therapy for S. aureus infections. IMPORTANCE We identified hibifolin as a sortase A (SrtA) inhibitor by screening the natural compounds library, which effectively inhibited the activity of SrtA with an IC50 value of 31.20 μg/mL. Hibifolin attenuated the pathogenic behavior of Staphylococcus aureus, including adhesion, invasion, and biofilm formation. Binding assays showed that hibifolin bound to SrtA protein directly. Hibifolin improved the survival of pneumonia induced by S. aureus USA300 in mice and alleviated the pathological damage. Moreover, hibifolin showed a synergistic antibacterial effect with cefotaxime in USA300-infected mice.
Keywords: cefotaxime; hibifolin; methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; pneumonia; sortase A.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Tkaczyk C, Hamilton MM, Sadowska A, Shi Y, Chang CS, Chowdhury P, Buonapane R, Xiao X, Warrener P, Mediavilla J, Kreiswirth B, Suzich J, Stover CK, Sellman BR. 2016. Targeting alpha toxin and ClfA with a multimechanistic monoclonal-antibody-based approach for prophylaxis of serious Staphylococcus aureus disease. mBio 7:e00528-16. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00528-16. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

