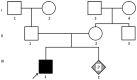
A novel CLCNKB variant in a Chinese family with classic Bartter syndrome and prenatal genetic diagnosis
- PMID: 35913199
- PMCID: PMC9544217
- DOI: 10.1002/mgg3.2027
A novel CLCNKB variant in a Chinese family with classic Bartter syndrome and prenatal genetic diagnosis
Abstract
Background: Type III Bartter syndrome (BS), often known as classic Bartter syndrome is caused by variants in CLCNKB gene, which encoding the basolateral chloride channel protein ClC-Kb, and is characterized by renal salt wasting, hypokalemia, metabolic alkalosis, increased renin, and aldosterone levels.
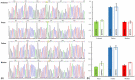
Methods: A 2-year-old boy presented severe malnutrition, severe metabolic alkalosis and severe hypokalemia and was clinically diagnosed with BS. The trio exome sequencing (ES) was performed to discover the genetic cause of this patient, followed by validation using Sanger sequencing and quantitative polymerase chain reaction subsequently.
Results: The genetic analysis indicated that this patient with a compound heterozygous variants of CLCNKB gene including a novel nonsense variant c.876 T > A and a whole-gene deletion. The two variants were inherited from his parents, respectively. Subsequently, target sequencing of CLCNKB gene was performed for next pregnancy, and prenatal genetic diagnosis was provided for the family.
Conclusions: The results of current study identified the compound heterozygous variants in a patient with classic BS. The novel variant expands the spectrum of CLCNKB variants in BS. Our study also indicates that ES is an alternative tool to simultaneously detect single-nucleotide variants and copy-number variants.
Keywords: CLCNKB; classic Bartter syndrome; exome sequencing; prenatal genetic diagnosis.
© 2022 The Authors. Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Bettinelli, A. , Borsa, N. , Bellantuono, R. , Syrèn, M. L. , Calabrese, R. , Edefonti, A. , Komninos, J. , Santostefano, M. , Beccaria, L. , Pela, I. , Bianchetti, M. G. , & Tedeschi, S. (2007). Patients with biallelic mutations in the chloride channel gene CLCNKB: Long‐term management and outcome. American Journal of Kidney Diseases, 49(1), 91–98. 10.1053/j.ajkd.2006.10.001 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Boone, P. M. , Campbell, I. M. , Baggett, B. C. , Soens, Z. T. , Rao, M. M. , Hixson, P. M. , Patel, A. , Bi, W. , Cheung, S. W. , Lalani, S. R. , Beaudet, A. L. , Stankiewicz, P. , Shaw, C. A. , & Lupski, J. R. (2013). Deletions of recessive disease genes: CNV contribution to carrier states and disease‐causing alleles. Genome Research, 23(9), 1383–1394. 10.1101/gr.156075.113 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

