The Toxicity and Antibacterial Effects of Povidone-Iodine Irrigation in Fracture Surgery
- PMID: 35913384
- PMCID: PMC9483079
- DOI: 10.1111/os.13422
The Toxicity and Antibacterial Effects of Povidone-Iodine Irrigation in Fracture Surgery
Abstract
Objective: Surgical site infection is a common complication of surgery, especially in orthopedics. Povidone-Iodine (PI) is one of the oldest and most commonly used disinfectants in surgery. However, the toxicity and antimicrobial effect of PI have not been discussed. In addition, no study has explored the optimum PI concentration for sterilization and tissue healing. This study explores the germicidal efficacy of different concentrations PI, in addition, the toxicity and antibacterial effects of PI irrigation in fracture surgery are also discussed.
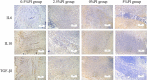
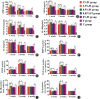
Methods: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa) were used to evaluate the germicidal efficacy of PI in vitro and in vivo. In vitro, the effects of PI on bacterial growth were analyzed. 2.5%, 1.25%, 0.5%, 0.25%, 0.05%, 0.025%, 0.005%, 0.0025% and 0% PI was added into the bacterial suspension, besides, the bacterial algebra and growth rate were tested. Meanwhile, the fluorescence intensity of viable bacteria was also tested to evaluate the effects of PI on bacterial survival. In vivo, first, femoral fracture with wound infection rat models were established. Second, thyroid gland sections, blood thyroxine, urinary iodine, wound local skin, muscle and bone tissue sections, serum creatinine and alanine aminotransferase, serum and bone local tissue interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-10 (IL-10), bone morphogenetic protein (BMP-2), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and transforming growth factor (TGF-β1) were detected in rat femoral shaft fracture model with 5%, 2.5%, 0.5%, 0.05%, and 0% PI irrigation. Third, tissue bacteria culture was tested in rat femoral fracture with wound infection model with different concentrations PI irrigation.
Results: In vitro, 2.5%, 1.25%, 0.5% PI inhibited the growth of bacteria. 1.25%, 0.5% PI killed all the bacteria, while 0.25%, 0.05% PI had not killed bacteria after about 10 min. The iodine absorption of 5%, 2.5%, 0.5% PI irrigation did not cause thyroid injury. The 5%, 2.5%, 0.5% PI irrigation did not make serum creatinine and alanine aminotransferase abnormal and can remove bacteria from wounds. The 0.5%, 2.5% PI irrigation can promote tissue healing and increase BMP-2, VEGF, TGF-β1, IL-10, in addition, decrease IL-6. 5% PI irrigation would inhibit tissue healing, and increase IL-6, decrease BMP-2, VEGF, TGF-β1, IL-10.
Conclusions: Povidone-Iodine was a widely used disinfectant and 2.5%, 1.25% and 0.5% PI could effectively kill bacteria. Five percent and lower concentration PI irrigation was safe and could not cause thyroid, kidney and liver damage. The 0.5% PI irrigation was beneficial for tissue healing but 5% PI irrigation was the opposite.
Keywords: Antibacterial properties; MRSA; Povidone-iodine irrigation; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Toxicity of povidone-iodine.
© 2022 The Authors. Orthopaedic Surgery published by Tianjin Hospital and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Chlorhexidine Antiseptic Irrigation Eradicates Staphylococcus epidermidis From Biofilm: An In Vitro Study.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2018 Mar;476(3):648-653. doi: 10.1007/s11999.0000000000000052. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2018. PMID: 29443852 Free PMC article.
-
Povidone-iodine ointment demonstrates in vitro efficacy against biofilm formation.Int Wound J. 2017 Feb;14(1):172-179. doi: 10.1111/iwj.12578. Epub 2016 Mar 10. Int Wound J. 2017. PMID: 26968574 Free PMC article.
-
Is EDTA Irrigation Effective in Reducing Bacterial Infection in a Rat Model of Contaminated Intra-articular Knee Implants?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2020 May;478(5):1111-1121. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000001119. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2020. PMID: 32012144 Free PMC article.
-
Dilute Povidone-Iodine Irrigation: The Science of Molecular Iodine (I2) Kinetics and Its Antimicrobial Activity.J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2025 Jan 15;33(2):65-73. doi: 10.5435/JAAOS-D-24-00471. Epub 2024 Oct 8. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2025. PMID: 39729104 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Povidone-iodine: use in hand disinfection, skin preparation and antiseptic irrigation.Int Wound J. 2008 Jun;5(3):376-87. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-481X.2007.00405.x. Int Wound J. 2008. PMID: 18593388 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immobilization of Bacteriophages in Ex Tempore Hydrogel for the Treatment of Burn Wound Infection.Gels. 2023 Aug 3;9(8):625. doi: 10.3390/gels9080625. Gels. 2023. PMID: 37623080 Free PMC article.
-
Topical betadine exposure precipitating sterile cerebritis and systemic iodine toxicity.Clin Case Rep. 2023 Jul 18;11(7):e7693. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.7693. eCollection 2023 Jul. Clin Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 37476593 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic iodine levels increase with povidone-iodine irrigation, but does this affect thyroid functions? A case-control study.J Orthop Surg Res. 2024 Oct 8;19(1):636. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-04877-8. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 39380015 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Antiseptic, Hemostatic, and Wound Activity of Poly(vinylpyrrolidone)-Iodine Gel with Trimethyl Chitosan.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 9;25(4):2106. doi: 10.3390/ijms25042106. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38396783 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Efficacy of Five Wound Irrigation Solutions in the Biofilm Microenvironment In Vitro and Ex Vivo.Antibiotics (Basel). 2025 Jan 3;14(1):25. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics14010025. Antibiotics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39858311 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ulivieri S, Toninelli S, Petrini C, Giorgio A, Oliveri G. Prevention of post‐operative infections in spine surgery by wound irrigation with a solution of povidone‐iodine and hydrogen peroxide. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2011;131(9):1203–6. - PubMed
-
- Cook GE, Markel DC, Ren W, Webb LX, McKee MD, Schemitsch EH et al Infection in orthopaedics. J Orthop Trauma 2015;29 Suppl 12:S19‐23. - PubMed
-
- Kanno E, Tanno H, Suzuki A, Kamimatsuno R, Tachi M. Reconsideration of iodine in wound irrigation: the effects on Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation. J Wound Care. 2016;25(6):335–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

