Analysis of a diffusive epidemic system with spatial heterogeneity and lag effect of media impact
- PMID: 35913603
- PMCID: PMC9340761
- DOI: 10.1007/s00285-022-01780-w
Analysis of a diffusive epidemic system with spatial heterogeneity and lag effect of media impact
Abstract
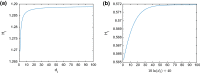
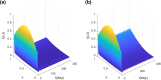
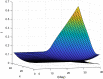
We considered an SIS functional partial differential model cooperated with spatial heterogeneity and lag effect of media impact. The wellposedness including existence and uniqueness of the solution was proved. We defined the basic reproduction number and investigated the threshold dynamics of the model, and discussed the asymptotic behavior and monotonicity of the basic reproduction number associated with the diffusion rate. The local and global Hopf bifurcation at the endemic steady state was investigated theoretically and numerically. There exists numerical cases showing that the larger the number of basic reproduction number, the smaller the final epidemic size. The meaningful conclusion generalizes the previous conclusion of ordinary differential equation.
Keywords: Functional partial differential model; Hopf bifurcation; Media impact; Spatial heterogeneity.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Figures
References
-
- Allen LJS, Bolker BM, Lou Y, Nevai AL. Asymptotic profiles of the steady states for an SIS epidemic reaction-diffusion model. Discrete Contin Dyn Syst Ser A. 2008;21(1):1–20. doi: 10.3934/dcds.2008.21.1. - DOI
-
- Anderson RM, May RM (1991) Infectious Diseases of Humans: Dynamics and Control. Cambridge University Press
-
- Busenberg S, Huang W. Stability and Hopf bifurcation for a population delay model with diffusion effects. J Differ Equ. 1996;124(1):80–107. doi: 10.1006/jdeq.1996.0003. - DOI
-
- Cantrell RS, Cosner C (2003) Spatial Ecology via Reaction-diffusion Equations. John Wiley and Sons Ltd, Chichester
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

