Apelin and its ratio to lipid factors are associated with cardiovascular diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 35913970
- PMCID: PMC9342781
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0271899
Apelin and its ratio to lipid factors are associated with cardiovascular diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The present systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to ascertain if the circulating levels of apelin, as an important regulator of the cardiovascular homeostasis, differ in patients with cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) and controls.
Methods: A comprehensive search was performed in electronic databases including PubMed, Scopus, EMBASE, and Web of Science to identify the studies addressing apelin in CVD up to April 5, 2021. Due to the presence of different units to measure the circulating levels of apelin across the included studies, they expressed the standardized mean difference (SMD) and their 95% confidence interval (CI) as summary effect size. A random-effects model comprising DerSimonian and Laird method was used to pool SMDs.
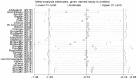
Results: Twenty-four articles (30 studies) comprised of 1793 cases and 1416 controls were included. Pooled results obtained through random-effects model indicated that apelin concentrations in the cases' blood samples were significantly lower than those of the control groups (SMD = -0.72, 95% CI: -1.25, -0.18, P = 0.009; I2 = 97.3%, P<0.001). New combined biomarkers showed a significant decrease in SMD of apelin/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (apelin/HDL-C) ratio [-5.17; 95% CI, -8.72, -1.63, P = 0.000; I2 = 99.0%], apelin/low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (apelin/LDL-C) ratio [-4.31; 95% CI, -6.08, -2.55, P = 0.000; I2 = 98.0%] and apelin/total cholesterol (apelin/TC) ratio [-17.30; 95% CI, -22.85, -11.76, P = 0.000; I2 = 99.1%]. However, no significant differences were found in the SMD of apelin/triacylglycerol (apelin/TG) ratio in cases with CVDs compared to the control group [-2.96; 95% CI, -7.41, 1.49, P = 0.000; I2 = 99.2%].
Conclusion: The association of apelin with CVDs is different based on the region and disease subtypes. These findings account for the possible usefulness of apelin as an additional biomarker in the diagnosis of CVD in diabetic patients and in the diagnosis of patients with CAD. Moreover, apelin/HDL-c, apelin/LDL-c, and apelin/TC ratios could be offered as diagnostic markers for CVD.
Conflict of interest statement
I have read the journal’s policy and have no conflicts.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of turmeric and curcumin in lowering blood lipid levels in patients with cardiovascular risk factors: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Nutr J. 2017 Oct 11;16(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s12937-017-0293-y. Nutr J. 2017. PMID: 29020971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid profile in girls with precocious puberty: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Endocr Disord. 2023 Oct 18;23(1):225. doi: 10.1186/s12902-023-01470-8. BMC Endocr Disord. 2023. PMID: 37848909 Free PMC article.
-
Apelin levels in pregnant women with and without gestational diabetes mellitus: a collaborative systematic review and meta-analysis.Gynecol Endocrinol. 2022 Oct;38(10):803-812. doi: 10.1080/09513590.2022.2114450. Epub 2022 Aug 24. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2022. PMID: 36002980
-
Association between blood lipid levels and risk of gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2023 Jul 7;18(7):e0288111. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0288111. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37418353 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Canola Oil Consumption on Lipid Profile: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Clinical Trials.J Am Coll Nutr. 2019 Feb;38(2):185-196. doi: 10.1080/07315724.2018.1475270. Epub 2018 Oct 31. J Am Coll Nutr. 2019. PMID: 30381009
Cited by
-
Effects of flaxseed supplementation on weight loss, lipid profiles, glucose, and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein in patients with coronary artery disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Clin Cardiol. 2024 Jan;47(1):e24211. doi: 10.1002/clc.24211. Clin Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38269632 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers of Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence in Patients with Paroxysmal or Persistent Atrial Fibrillation Following External Direct Current Electrical Cardioversion.Biomedicines. 2023 May 16;11(5):1452. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11051452. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37239123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigation of Genetic Variations in APLN and APLNR Genes and Their Potential Role in Cardiovascular Diseases.Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2025 Jan;13(4):525-539. doi: 10.61186/rbmb.13.4.525. Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40842897 Free PMC article.
-
Negative association of apelin plasma levels with epicardial fat thickness in patients with stable angina and acute myocardial infarction: A case-control study.J Res Med Sci. 2024 Jul 11;29:26. doi: 10.4103/jrms.jrms_478_22. eCollection 2024. J Res Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39239076 Free PMC article.
-
Apelin-to-total cholesterol ratio predicts long-term major adverse cardiovascular events in ST-elevation myocardial infarction patients after primary percutaneous coronary intervention: a retrospective cohort analysis.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2025 Jul 4;25(1):478. doi: 10.1186/s12872-025-04949-5. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2025. PMID: 40615939 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kheirmand Parizi M, Akbari H, Malek-Mohamadi M, Kheirmand Parizi M, Kakoei S. Association of salivary levels of immunoglobulin-a and amylase with oral-dental manifestations in patients with controlled and non-controlled type 2 diabetes. BMC oral health. 2019;19(1):175. Epub 2019/08/08. doi: 10.1186/s12903-019-0868-4 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

