Nanoflow Sheath Voltage-Free Interfacing of Capillary Electrophoresis and Mass Spectrometry for the Detection of Small Molecules
- PMID: 35913997
- PMCID: PMC9387528
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.2c02074
Nanoflow Sheath Voltage-Free Interfacing of Capillary Electrophoresis and Mass Spectrometry for the Detection of Small Molecules
Abstract
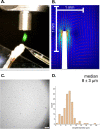
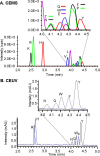
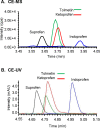
Coupling capillary electrophoresis (CE) to mass spectrometry (MS) is a powerful strategy to leverage a high separation efficiency with structural identification. Traditional CE-MS interfacing relies upon voltage to drive this process. Additionally, sheathless interfacing requires that the electrophoresis generates a sufficient volumetric flow to sustain the ionization process. Vibrating sharp-edge spray ionization (VSSI) is a new method to interface capillary electrophoresis to mass analyzers. In contrast to traditional interfacing, VSSI is voltage-free, making it straightforward for CE and MS. New nanoflow sheath CE-VSSI-MS is introduced in this work to reduce the reliance on the separation flow rate to facilitate the transfer of analyte to the MS. The nanoflow sheath VSSI spray ionization functions from 400 to 900 nL/min. Using the new nanoflow sheath reported here, volumetric flow rate through the separation capillary is less critical, allowing the use of a small (i.e., 20 to 25 μm) inner diameter separation capillary and enabling the use of higher separation voltages and faster analysis. Moreover, the use of a nanoflow sheath enables greater flexibility in the separation conditions. The nanoflow sheath is operated using aqueous solutions in the background electrolyte and in the sheath, demonstrating the separation can be performed under normal and reversed polarity in the presence or absence of electroosmotic flow. This includes the use of a wider pH range as well. The versatility of nanoflow sheath CE-VSSI-MS is demonstrated by separating cationic, anionic, and zwitterionic molecules under a variety of separation conditions. The detection sensitivity observed with nanoflow sheath CE-VSSI-MS is comparable to that obtained with sheathless CE-VSSI-MS as well as CE-MS separations with electrospray ionization interfacing. A bare fused silica capillary is used to separate cationic β-blockers with a near-neutral background electrolyte at concentrations ranging from 1.0 nM to 1.0 μM. Under acidic conditions, 13 amino acids are separated with normal polarity at a concentration ranging from 0.25 to 5 μM. Finally, separations of anionic compounds are demonstrated using reversed polarity under conditions of suppressed electroosmotic flow through the use of a semipermanent surface coating. With a near-neutral separation electrolyte, anionic nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are detected over a concentration range of 0.1 to 5.0 μM.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Protein analysis using capillary electrophoresis coupled to mass spectrometry through vibrating sharp-edge spray ionization.Electrophoresis. 2024 Sep;45(17-18):1597-1605. doi: 10.1002/elps.202300298. Epub 2024 Apr 5. Electrophoresis. 2024. PMID: 38577828
-
Low Flow Voltage Free Interface for Capillary Electrophoresis and Mass Spectrometry Driven by Vibrating Sharp-Edge Spray Ionization.Anal Chem. 2020 Feb 18;92(4):3006-3013. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.9b03994. Epub 2020 Feb 7. Anal Chem. 2020. PMID: 31971372 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of a nanoflow sheath liquid interface and comparison to a sheath liquid and a sheathless porous-tip interface for CE-ESI-MS in positive and negative ionization.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2018 Aug;410(21):5265-5275. doi: 10.1007/s00216-018-1179-3. Epub 2018 Jun 26. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2018. PMID: 29943266
-
[Capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry and its application to proteomic analysis].Se Pu. 2020 Oct 8;38(10):1117-1124. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2020.03005. Se Pu. 2020. PMID: 34213108 Review. Chinese.
-
[Analysis of metabolomics and proteomics based on capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry].Se Pu. 2020 Sep 8;38(9):1013-1021. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2020.02025. Se Pu. 2020. PMID: 34213267 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Acoustofluidics: Technology Advances and Applications from 2022 to 2024.Anal Chem. 2025 Apr 8;97(13):6847-6870. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.4c06803. Epub 2025 Mar 25. Anal Chem. 2025. PMID: 40133046 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Unravelling lipid heterogeneity: Advances in single-cell lipidomics in cellular metabolism and disease.BBA Adv. 2025 Jun 27;8:100169. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadva.2025.100169. eCollection 2025. BBA Adv. 2025. PMID: 40678619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Direct sub-atmospheric pressure ionization mass spectrometry: Evaporation/sublimation-driven ionization is amazing, fundamentally, and practically.J Mass Spectrom. 2024 Jun;59(6):e5018. doi: 10.1002/jms.5018. J Mass Spectrom. 2024. PMID: 38736378 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spatially blocked split CRISPR-Cas12a system for ultra-sensitive and versatile small molecule activation and detection.Nat Commun. 2025 May 30;16(1):5035. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-60265-8. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40447601 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative study of the vibrating capillary nebulizer (VCN) and commercially available interfaces for on-line coupling of capillary electrophoresis with ICP-MS.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2024 Mar;416(7):1613-1621. doi: 10.1007/s00216-024-05162-7. Epub 2024 Jan 29. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2024. PMID: 38285228
References
-
- Kawai T.; Ota N.; Okada K.; Imasato A.; Owa Y.; Morita M.; Tada M.; Tanaka Y. Ultrasensitive Single Cell Metabolomics by Capillary Electrophoresis-Mass Spectrometry with a Thin-Walled Tapered Emitter and Large-Volume Dual Sample Preconcentration. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 10564–10572. 10.1021/acs.analchem.9b01578. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

