Life-long dietary restrictions have negligible or damaging effects on late-life cognitive performance: A key role for genetics in outcomes
- PMID: 35914473
- PMCID: PMC9583241
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2022.07.004
Life-long dietary restrictions have negligible or damaging effects on late-life cognitive performance: A key role for genetics in outcomes
Abstract
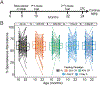
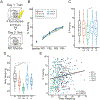
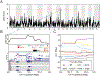
Several studies report that caloric restriction (CR) or intermittent fasting (IF) can improve cognition, while others report limited or no cognitive benefits. Here, we compare the effects of 20% CR, 40% CR, 1-day IF, and 2-day IF feeding paradigms to ad libitum controls on Y-maze working memory (WM) and contextual fear memory (CFM) in a large population of Diversity Outbred mice that model the genetic diversity of humans. While CR and IF interventions improve lifespan, we observed no enhancement of working memory or CFM in mice on these feeding paradigms, and report 40% CR to be damaging to recall of CFM. Using Quantitative Trait Loci mapping, we identified the gene Slc16a7 to be associated with CFM outcomes in aged mice on lifespan promoting feeding paradigms. Limited utility of dieting and fasting on memory in mice that recapitulate genetic diversity in the human population highlights the need for anti-aging therapeutics that promote cognitive function, with the neuronal monocarboxylate transporter MCT2 encoded by Slc16a7 highlighted as novel target.
Keywords: Caloric restriction; Cognition; Genetic diversity; Intermittent fasting; Metabolism.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lifelong caloric restriction increases working memory in mice.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 10;8(7):e68778. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068778. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23874758 Free PMC article.
-
Daily Fasting Improves Health and Survival in Male Mice Independent of Diet Composition and Calories.Cell Metab. 2019 Jan 8;29(1):221-228.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2018.08.011. Epub 2018 Sep 6. Cell Metab. 2019. PMID: 30197301 Free PMC article.
-
Intermittent fasting and caloric restriction interact with genetics to shape physiological health in mice.Genetics. 2022 Jan 4;220(1):iyab157. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyab157. Genetics. 2022. PMID: 34791228 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of caloric and dietary restriction regimens on markers of health and longevity in humans and animals: a summary of available findings.Nutr J. 2011 Oct 7;10:107. doi: 10.1186/1475-2891-10-107. Nutr J. 2011. PMID: 21981968 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of Lifespan Regulation by Calorie Restriction and Intermittent Fasting in Model Organisms.Nutrients. 2020 Apr 24;12(4):1194. doi: 10.3390/nu12041194. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32344591 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Brain responses to intermittent fasting and the healthy living diet in older adults.Cell Metab. 2024 Aug 6;36(8):1668-1678.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2024.05.017. Epub 2024 Jun 19. Cell Metab. 2024. PMID: 38901423 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Vital Role of Visceral Adipose Tissue in Maintaining Cognitive Functions.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 9;26(14):6597. doi: 10.3390/ijms26146597. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40724847 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in adult and aged genetically diverse mice.Geroscience. 2025 Jun 17. doi: 10.1007/s11357-025-01749-9. Online ahead of print. Geroscience. 2025. PMID: 40526250
References
-
- Bates D, Mächler M, Bolker B, Walker S, 2015. Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J. Stat. Softw 1 (1), 2015.
-
- Bolivar VJ, Pooler O, Flaherty L, 2001. Inbred strain variation in contextual and cued fear conditioning behavior. Mamm. Genome 12 (8), 651–656. - PubMed
-
- Burger JM, Buechel SD, Kawecki TJ, 2010. Dietary restriction affects lifespan but not cognitive aging in Drosophila melanogaster. Aging Cell 9 (3), 327–335. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

