Variability of cross-tissue X-chromosome inactivation characterizes timing of human embryonic lineage specification events
- PMID: 35914524
- PMCID: PMC9398941
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2022.07.007
Variability of cross-tissue X-chromosome inactivation characterizes timing of human embryonic lineage specification events
Abstract
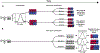
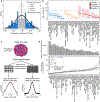
X-chromosome inactivation (XCI) is a random, permanent, and developmentally early epigenetic event that occurs during mammalian embryogenesis. We harness these features to investigate characteristics of early lineage specification events during human development. We initially assess the consistency of X-inactivation and establish a robust set of XCI-escape genes. By analyzing variance in XCI ratios across tissues and individuals, we find that XCI is shared across all tissues, suggesting that XCI is completed in the epiblast (in at least 6-16 cells) prior to specification of the germ layers. Additionally, we exploit tissue-specific variability to characterize the number of cells present during tissue-lineage commitment, ranging from approximately 20 cells in liver and whole blood tissues to 80 cells in brain tissues. By investigating the variability of XCI ratios using adult tissue, we characterize embryonic features of human XCI and lineage specification that are otherwise difficult to ascertain experimentally.
Keywords: X-chromosome inactivation; allele-specific expression; developmental lineage; embryonic stochasticity; escape from XCI; human development.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Eutherian mammals use diverse strategies to initiate X-chromosome inactivation during development.Nature. 2011 Apr 21;472(7343):370-4. doi: 10.1038/nature09872. Epub 2011 Apr 6. Nature. 2011. PMID: 21471966
-
[Initiation of X chromosome inactivation during early embryogenesis in mice and in humans].Bull Acad Natl Med. 2013 Mar;197(3):609-17. Bull Acad Natl Med. 2013. PMID: 25163344 Review. French.
-
Modeling X chromosome inactivation using t5iLA naive human pluripotent stem cells.BMC Biol. 2024 Sep 18;22(1):210. doi: 10.1186/s12915-024-01994-y. BMC Biol. 2024. PMID: 39294757 Free PMC article.
-
Escape from X-inactivation in twins exhibits intra- and inter-individual variability across tissues and is heritable.PLoS Genet. 2023 Feb 21;19(2):e1010556. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010556. eCollection 2023 Feb. PLoS Genet. 2023. PMID: 36802379 Free PMC article.
-
X chromosome inactivation in human pluripotent stem cells as a model for human development: back to the drawing board?Hum Reprod Update. 2017 Sep 1;23(5):520-532. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmx015. Hum Reprod Update. 2017. PMID: 28582519 Review.
Cited by
-
Stochasticity in genetics and gene regulation.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2024 Apr 22;379(1900):20230476. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2023.0476. Epub 2024 Mar 4. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38432316 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The transcriptional legacy of developmental stochasticity.Nat Commun. 2023 Nov 9;14(1):7226. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-43024-5. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37940702 Free PMC article.
-
Escape of Kdm6a from X chromosome is detrimental to ischemic brains via IRF5 signaling.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 27:rs.3.rs-4986866. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4986866/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: Transl Stroke Res. 2025 Jan 3. doi: 10.1007/s12975-024-01321-1. PMID: 39399684 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
High-coverage allele-resolved single-cell DNA methylation profiling reveals cell lineage, X-inactivation state, and replication dynamics.Nat Commun. 2025 Jul 8;16(1):6273. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-61589-1. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40624041 Free PMC article.
-
Jpx RNA controls Xist induction through spatial reorganization of the mouse X-inactivation center.Dev Cell. 2025 Jul 11:S1534-5807(25)00406-X. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2025.06.028. Online ahead of print. Dev Cell. 2025. PMID: 40680737
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

