Gut Microbiome in Colorectal Cancer: Clinical Diagnosis and Treatment
- PMID: 35914737
- PMCID: PMC10372906
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gpb.2022.07.002
Gut Microbiome in Colorectal Cancer: Clinical Diagnosis and Treatment
Abstract
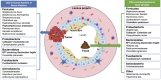
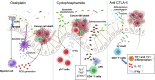
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most frequently diagnosed cancers and the leading cause of cancer-associated deaths. Epidemiological studies have shown that both genetic and environmental risk factors contribute to the development of CRC. Several metagenomic studies of CRC have identified gut dysbiosis as a fundamental risk factor in the evolution of colorectal malignancy. Although enormous efforts and substantial progresses have been made in understanding the relationship between human gut microbiome and CRC, the precise mechanisms involved remain elusive. Recent data have shown a direct causative role of the gut microbiome in DNA damage, inflammation, and drug resistance in CRC, suggesting that modulation of gut microbiome could act as a powerful tool in CRC prevention and therapy. Here, we provide an overview of the relationship between gut microbiome and CRC, and explore relevant mechanisms of colorectal tumorigenesis. We next highlight the potential of bacterial species as clinical biomarkers, as well as their roles in therapeutic response. Factors limiting the clinical translation of gut microbiome and strategies for resolving current challenges are further discussed.
Keywords: Chemotherapy; Colorectal cancer; Diagnostic biomarker; Gut microbiome; Immunotherapy.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel R.L., Miller K.D., Fuchs H.E., Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 2022;72:7–33. - PubMed
-
- Czene K., Lichtenstein P., Hemminki K. Environmental and heritable causes of cancer among 9.6 million individuals in the Swedish family-cancer database. Int J Cancer. 2002;99:260–266. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

