Extracellular vesicles: emerging anti-cancer drugs and advanced functionalization platforms for cancer therapy
- PMID: 35915054
- PMCID: PMC9347476
- DOI: 10.1080/10717544.2022.2104404
Extracellular vesicles: emerging anti-cancer drugs and advanced functionalization platforms for cancer therapy
Abstract
Increasing evidences show that unmodified extracellular vesicles (EVs) derived from various cells can effectively inhibit the malignant progression of different types of tumors by delivering the bioactive molecules. Therefore, EVs are expected to be developed as emerging anticancer drugs. Meanwhile, unmodified EVs as an advanced and promising nanocarrier that is frequently used in targeted delivery therapeutic cargos and personalized reagents for the treatment and diagnosis of cancer. To improve the efficacy of EV-based treatments, researchers are trying to engineering EVs as an emerging nanomedicine translational therapy platform through biological, physical and chemical approaches, which can be broaden and altered to enhance their therapeutic capability. EVs loaded with therapeutic components such as tumor suppressor drugs, siRNAs, proteins, peptides, and conjugates exhibit significantly enhanced anti-tumor effects. Moreover, the design and preparation of tumor-targeted modified EVs greatly enhance the specificity and effectiveness of tumor therapy, and these strategies are expected to become novel ideas for tumor precision medicine. This review will focus on reviewing the latest research progress of functionalized EVs, clarifying the superior biological functions and powerful therapeutic potential of EVs, for researchers to explore new design concepts based on EVs and build next-generation nanomedicine therapeutic platforms.
Keywords: Engineered EVs; bioinspiration; cancer therapy; drug delivery; functionalization strategy.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures


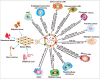

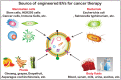

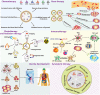
References
-
- Altanerova U, Jakubechova J, Benejova K, et al. (2019). Prodrug suicide gene therapy for cancer targeted intracellular by mesenchymal stem cell exosomes. Int J Cancer 144:897–908. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez-Erviti L, Seow Y, Yin H, et al. (2011). Delivery of siRNA to the mouse brain by systemic injection of targeted exosomes. Nat Biotechnol 29:341–5. - PubMed
-
- Aqil F, Munagala R, Jeyabalan J, et al. (2017). Exosomes for the enhanced tissue bioavailability and efficacy of curcumin. Aaps J 19:1691–702. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
