Early life adversity shapes neural circuit function during sensitive postnatal developmental periods
- PMID: 35915071
- PMCID: PMC9343623
- DOI: 10.1038/s41398-022-02092-9
Early life adversity shapes neural circuit function during sensitive postnatal developmental periods
Abstract
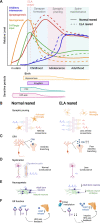
Early life adversity (ELA) is a major risk factor for mental illness, but the neurobiological mechanisms by which ELA increases the risk for future psychopathology are still poorly understood. Brain development is particularly malleable during prenatal and early postnatal life, when complex neural circuits are being formed and refined through an interplay of excitatory and inhibitory neural input, synaptogenesis, synaptic pruning, myelination, and neurogenesis. Adversity that influences these processes during sensitive periods of development can thus have long-lasting and pervasive effects on neural circuit maturation. In this review, we will discuss clinical and preclinical evidence for the impact of ELA on neural circuit formation with a focus on the early postnatal period, and how long-lasting impairments in these circuits can affect future behavior. We provide converging evidence from human and animal studies on how ELA alters the functional development of brain regions, neural circuits, and neurotransmitter systems that are crucial for cognition and affective behavior, including the hippocampus, the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, neural networks of fear responses and cognition, and the serotonin (5-HT) system. We also discuss how gene-by-environment (GxE) interactions can determine individual differences in susceptibility and resilience to ELA, as well as molecular pathways by which ELA regulates neural circuit development, for which we emphasize epigenetic mechanisms. Understanding the molecular and neurobiological mechanisms underlying ELA effects on brain function and psychopathology during early postnatal sensitive periods may have great potential to advance strategies to better treat or prevent psychiatric disorders that have their origin early in life.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
CA has received research funding from Sunovion Pharmaceuticals, and has consulted for Ono Pharmaceuticals. None of these potential conflicts of interest are related to the subject matter discussed in this review, and they have not influenced the content of this review.
Figures


References
-
- Merrick MT, Ford DC, Ports KA, Guinn AS, Chen J, Klevens J, et al. Vital signs: estimated proportion of adult health problems attributable to adverse childhood experiences and implications for prevention—25 States, 2015-2017. Morbidity Mortal Wkly Rep. 2019;68:999–1005. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6844e1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Felitti VJ, Anda RF, Nordenberg D, Williamson DF, Spitz AM, Edwards V, et al. Relationship of childhood abuse and household dysfunction to many of the leading causes of death in adults. The Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACE) Study. Am J Prev Med. 1998;14:245–58. doi: 10.1016/S0749-3797(98)00017-8. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Green JG, McLaughlin KA, Berglund PA, Gruber MJ, Sampson NA, Zaslavsky AM, et al. Childhood adversities and adult psychiatric disorders in the national comorbidity survey replication I: associations with first onset of DSM-IV disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2010;67:113–23. doi: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2009.186. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

