Profiling of gene expression in the brain associated with anxiety-related behaviors in the chronic phase following cranial irradiation
- PMID: 35915120
- PMCID: PMC9343641
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-17310-z
Profiling of gene expression in the brain associated with anxiety-related behaviors in the chronic phase following cranial irradiation
Abstract
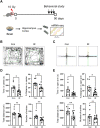
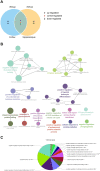
Although the brain is exposed to cranial irradiation in many clinical contexts, including malignant brain tumor therapy, such exposure can cause delayed neuropsychiatric disorders in the chronic phase. However, how specific molecular mechanisms are associated with irradiation-induced behavioral dysfunction, especially anxiety-like behaviors, is unclear. In the present study, we evaluated anxiety-like behaviors in adult C57BL/6 mice using the open-field (OF) and elevated plus maze (EPM) tests 3 months following single cranial irradiation (10 Gy). Additionally, by using RNA sequencing (RNA-seq), we analyzed gene expression profiles in the cortex and hippocampus of the adult brain to demonstrate the molecular mechanisms of radiation-induced brain dysfunction. In the OF and EPM tests, mice treated with radiation exhibited increased anxiety-like behaviors in the chronic phase. Gene expression analysis by RNA-seq revealed 89 and 106 differentially expressed genes in the cortex and hippocampus, respectively, following cranial irradiation. Subsequently, ClueGO and STRING analyses clustered these genes in pathways related to protein kinase activity, circadian behavior, and cell differentiation. Based on our expression analysis, we suggest that behavioral dysfunction following cranial irradiation is associated with altered expression of Cdkn1a, Ciart, Fos, Hspa5, Hspb1 and Klf10. These novel findings may provide potential genetic targets to investigate for the development of radioprotective agents.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Laperriere, N., Zuraw, L., Cairncross, G. & Cancer Care Ontario Practice Guidelines Initiative Neuro-Oncology Disease Site, G. Radiotherapy for newly diagnosed malignant glioma in adults: a systematic review. Radiother Oncol64, 259–273, doi:10.1016/s0167-8140(02)00078-6 (2002). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

