Large-scale genome-wide association study of coronary artery disease in genetically diverse populations
- PMID: 35915156
- PMCID: PMC9419655
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-022-01891-3
Large-scale genome-wide association study of coronary artery disease in genetically diverse populations
Abstract
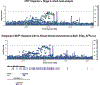
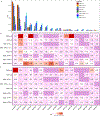
We report a genome-wide association study (GWAS) of coronary artery disease (CAD) incorporating nearly a quarter of a million cases, in which existing studies are integrated with data from cohorts of white, Black and Hispanic individuals from the Million Veteran Program. We document near equivalent heritability of CAD across multiple ancestral groups, identify 95 novel loci, including nine on the X chromosome, detect eight loci of genome-wide significance in Black and Hispanic individuals, and demonstrate that two common haplotypes at the 9p21 locus are responsible for risk stratification in all populations except those of African origin, in which these haplotypes are virtually absent. Moreover, in the largest GWAS for angiographically derived coronary atherosclerosis performed to date, we find 15 loci of genome-wide significance that robustly overlap with established loci for clinical CAD. Phenome-wide association analyses of novel loci and polygenic risk scores (PRSs) augment signals related to insulin resistance, extend pleiotropic associations of these loci to include smoking and family history, and precisely document the markedly reduced transferability of existing PRSs to Black individuals. Downstream integrative analyses reinforce the critical roles of vascular endothelial, fibroblast, and smooth muscle cells in CAD susceptibility, but also point to a shared biology between atherosclerosis and oncogenesis. This study highlights the value of diverse populations in further characterizing the genetic architecture of CAD.
© 2022. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics declarations - Competing interests
A.B. and L.A.L. are employees of Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. R.D. has received grants from AstraZeneca, grants and nonfinancial support from Goldfinch Bio, being a scientific co-founder, consultant and equity holder for Pensieve Health and being a consultant for Variant Bio. T. M. M. is an employee of the Healthcare Innovation Lab at BJC HealthCare / Washington University School of Medicine, an advisor of Myia Labs, and a compensated director the J.F Maddox Foundation in New Mexico. S.K. is an is an employee of Verve Therapeutics, holds equity in Verve Therapeutics and Maze Therapeutics, and has served as a consultant for Acceleron, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Novo Ventures, Ionis, Alnylam, Aegerion, Haug Partners, Noble Insights, Leerink Partners, Bayer Healthcare, Illumina, Color Genomics, MedGenome, Quest, and Medscape. D.J.R. is on the Scientific Advisory Board of Alnylam, Novartis, and Verve Therapeutics. M.D.R. is on the scientific advisory board for Goldfinch Bio and Cipherome. C.J.O became an employee of Novartis after initial submission of manuscript. P.N. reports investigator-initiated grants from Amgen, Apple, AstraZeneca, Boston Scientific, and Novartis, personal fees from Apple, AstraZeneca, Blackstone Life Sciences, Invitae, Foresite Labs, Novartis, Roche / Genentech, is a co-founder of TenSixteen Bio, is a shareholder of geneXwell, TenSixteen Bio, and Vertex, scientific advisory board member of geneXwell and TenSixteen Bio, and spousal employment at Vertex, all unrelated to the present work. S.M.D. receives research support from RenalytixAI to his institution and consulting fees from Calico Labs. A.G.B. is a scientific co-founder and equity holder in TenSixteen Bio. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

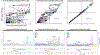





References
-
- Statistics;, N.C.f.H. Health, United States Spotlight: Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Heart Disease (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2019).
-
- Churchwell K et al. Call to Action: Structural Racism as a Fundamental Driver of Health Disparities: A Presidential Advisory From the American Heart Association. Circulation 142, e454–e468 (2020). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U01 HG004424/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100012C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007417/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG006385/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL103612/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100001I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085080/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG008676/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 DK126194/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG006375/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007419/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004438/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK101478/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX004821/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- R01 HL120393/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA229110/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG011172/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100010C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL080295/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004790/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100004I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM124836/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005G/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085082/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007416/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG008657/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL130114/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG006382/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200800007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL085251/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL139865/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085083/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085086/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD028685/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100046C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG011719/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004603/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL142302/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100003C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007376/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087652/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL127564/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG006389/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK101478/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004609/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL142017/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG008672/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL142711/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004599/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG008684/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 AG000989/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100006C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG006828/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201200036C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201800001C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG008679/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- IK2 CX001780/CX/CSRD VA/United States
- R01 HL151152/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN271201100004C/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG006380/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055222/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK114183/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX003340/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- U01 HG008666/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085079/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100002C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92021D00006/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG006388/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX003362/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- U01 HG008680/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 HL150186/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG006378/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK134575/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007843/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004610/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100003I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG008673/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100002I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG008685/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG006379/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023629/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001881/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG008664/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007397/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004608/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100001C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA164973/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL148050/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085081/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100004C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG008701/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG006830/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

