Genome-wide identification and characterization of the bHLH gene family and analysis of their potential relevance to chlorophyll metabolism in Raphanus sativus L
- PMID: 35915410
- PMCID: PMC9344636
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-022-08782-4
Genome-wide identification and characterization of the bHLH gene family and analysis of their potential relevance to chlorophyll metabolism in Raphanus sativus L
Abstract
Background: Green-fleshed radish (Raphanus sativus L.) is an economically important root vegetable of the Brassicaceae family, and chlorophyll accumulates in its root tissues. It was reported that the basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factors play vital roles in the process of chlorophyll metabolism. Nevertheless, a comprehensive study on the bHLH gene family has not been performed in Raphanus sativus L.
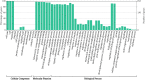
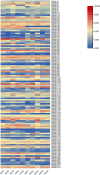
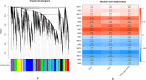
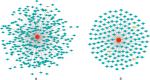
Results: In this study, a total of 213 Raphanus sativus L. bHLH (RsbHLH) genes were screened in the radish genome, which were grouped into 22 subfamilies. 204 RsbHLH genes were unevenly distributed on nine chromosomes, and nine RsbHLH genes were located on the scaffolds. Gene structure analysis showed that 25 RsbHLH genes were intron-less. Collineation analysis revealed the syntenic orthologous bHLH gene pairs between radish and Arabidopsis thaliana/Brassica rapa/Brassica oleracea. 162 RsbHLH genes were duplicated and retained from the whole genome duplication event, indicating that the whole genome duplication contributed to the expansion of the RsbHLH gene family. RNA-seq results revealed that RsbHLH genes had a variety of expression patterns at five development stages of green-fleshed radish and white-fleshed radish. In addition, the weighted gene co-expression network analysis confirmed four RsbHLH genes closely related to chlorophyll content.
Conclusions: A total of 213 RsbHLH genes were identified, and we systematically analyzed their gene structure, evolutionary and collineation relationships, conserved motifs, gene duplication, cis-regulatory elements and expression patterns. Finally, four bHLH genes closely involved in chlorophyll content were identified, which may be associated with the photosynthesis of the green-fleshed radish. The current study would provide valuable information for further functional exploration of RsbHLH genes, and facilitate clarifying the molecular mechanism underlying photosynthesis process in green-fleshed radish.
Keywords: Basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor; Chlorophyll content; Photosynthesis; Raphanus sativus L.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Genome-wide identification and characterization of NBS-encoding genes in Raphanus sativus L. and their roles related to Fusarium oxysporum resistance.BMC Plant Biol. 2021 Jan 18;21(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s12870-020-02803-8. BMC Plant Biol. 2021. PMID: 33461498 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification and characterization of CONSTANS-like gene family in radish (Raphanus sativus).PLoS One. 2018 Sep 24;13(9):e0204137. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0204137. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30248137 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification, characterization, and evolutionary analysis of flowering genes in radish (Raphanus sativus L.).BMC Genomics. 2017 Dec 19;18(1):981. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-4377-z. BMC Genomics. 2017. PMID: 29258434 Free PMC article.
-
Genes encoding pentatricopeptide repeat (PPR) proteins are not conserved in location in plant genomes and may be subject to diversifying selection.BMC Genomics. 2007 May 23;8:130. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-130. BMC Genomics. 2007. PMID: 17521445 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deciphering the Nutraceutical Potential of Raphanus sativus-A Comprehensive Overview.Nutrients. 2019 Feb 14;11(2):402. doi: 10.3390/nu11020402. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 30769862 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-Wide Analysis of bHLH Family Genes and Identification of Members Associated with Cold/Drought-Induced Photoinhibition in Kandelia obovata.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 3;24(21):15942. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115942. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958925 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive characterization and expression analysis of enzymatic antioxidant gene families in passion fruit (Passiflora edulis).iScience. 2023 Oct 26;26(11):108329. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108329. eCollection 2023 Nov 17. iScience. 2023. PMID: 38026217 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Defense Responses of Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) to Environmental Stress and CRISPR/Cas-Mediated Engineering of Stress Tolerance.Plants (Basel). 2025 Jun 28;14(13):1983. doi: 10.3390/plants14131983. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40647992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Basic Helix-Loop-Helix Transcription Factors: Regulators for Plant Growth Development and Abiotic Stress Responses.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 11;24(2):1419. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021419. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36674933 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-Wide Identification of bHLH Transcription Factor Family in Malus sieversii and Functional Exploration of MsbHLH155.1 Gene under Valsa Canker Infection.Plants (Basel). 2023 Jan 31;12(3):620. doi: 10.3390/plants12030620. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36771705 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

