Age- and sex-dependent differences in the morphology and composition of paraspinal muscles between subjects with and without lumbar degenerative diseases
- PMID: 35915426
- PMCID: PMC9341069
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-022-05692-0
Age- and sex-dependent differences in the morphology and composition of paraspinal muscles between subjects with and without lumbar degenerative diseases
Abstract
Background: The quality of the paraspinal muscles has been recommended as a surrogate marker for the evaluation of the severity of the lumbar degenerative diseases (LDD). The purpose of this study is to determine the age- and sex-dependent differences in the morphology and composition of the paraspinal muscles between LDD and asymptomatic subjects.
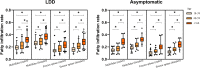
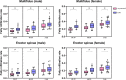
Methods: We analyzed data from 370 patients and 327 asymptomatic volunteers aged between 18-85 years. The measurement of the cross-sectional area (CSA) of the erector spinae, multifidus, and psoas at the L4/5-disc level was performed by the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The fatty infiltration ratio (FI %) of the multifidus and erector spinae was calculated.
Results: FI % of the lumbar paraspinal muscles were significantly and positively correlated with the severity of LDD instead of the CSA. Males had greater CSA than females, and females showed higher FI % than males in the paraspinal muscles. With the increase of age, the CSA of the lumbar paraspinal muscles gradually decreased, and the psoas showed the most significant decreasing trend. However, the FI % gradually increased in both LDD and asymptomatic groups with aging.
Conclusion: Age- and sex-dependent differences were found in the morphology and composition of the paraspinal muscles between subjects with and without LDD. Further long-term follow up investigations and basic studies will continue to confirm the natural history of the paraspinal muscles with aging and their association with LDD.
Keywords: Age- and sex-dependent differences; Asymptomatic subjects; Low back pain; Lumbar degenerative disease; Paraspinal muscles.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no financial and non-financial competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Is a single-level measurement of paraspinal muscle fat infiltration and cross-sectional area representative of the entire lumbar spine?Skeletal Radiol. 2018 Jul;47(7):939-945. doi: 10.1007/s00256-018-2902-z. Epub 2018 Feb 23. Skeletal Radiol. 2018. PMID: 29476224
-
[Radiographic parameters and influencing factors of paraspinal muscle degeneration in healthy people].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2024 Jul 15;38(7):880-888. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202402060. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39013828 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
MRI-defined paraspinal muscle morphology in Japanese population: The Wakayama Spine Study.PLoS One. 2017 Nov 8;12(11):e0187765. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0187765. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29117256 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging Evaluation of Fat Infiltration in Paraspinal Muscles on MRI: A Systematic Review with a Focus on Methodology.Orthop Surg. 2021 Jun;13(4):1141-1148. doi: 10.1111/os.12962. Epub 2021 May 4. Orthop Surg. 2021. PMID: 33942525 Free PMC article.
-
Paraspinal Muscles of Patients with Lumbar Diseases.J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg. 2018 Jul;79(4):323-329. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1639332. Epub 2018 Apr 16. J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg. 2018. PMID: 29660747 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of muscle degeneration and spinal balance in the pathophysiology of lumbar spinal stenosis: Study protocol of a translational approach combining in vivo biomechanical experiments with clinical and radiological parameters.PLoS One. 2023 Oct 27;18(10):e0293435. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0293435. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37889898 Free PMC article.
-
Risk Factors in Patients with Low Back Pain Under 40 Years Old: Quantitative Analysis Based on Computed Tomography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging mDIXON-Quant.J Pain Res. 2023 Oct 9;16:3417-3431. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S426488. eCollection 2023. J Pain Res. 2023. PMID: 37841453 Free PMC article.
-
Vertebral bone quality score was associated with paraspinal muscles fat infiltration, but not modic classification in patients with chronic low back pain: a prospective cross-sectional study.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024 Jul 3;25(1):509. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-07626-4. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024. PMID: 38956545 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Standing and Sitting Postures on Spinal Curvature and Muscle Mechanical Properties in Young Women: A Photogrammetric and MyotonPro Analysis.Med Sci Monit. 2024 Jul 29;30:e944930. doi: 10.12659/MSM.944930. Med Sci Monit. 2024. PMID: 39069714 Free PMC article.
-
Incidence and Risk Factors of Lumbosacral Complications Following Long-Segment Spinal Fusion in Adult Degenerative Scoliosis.Orthop Surg. 2025 Jan;17(1):133-140. doi: 10.1111/os.14275. Epub 2024 Oct 28. Orthop Surg. 2025. PMID: 39467685 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

