An interpretable neural network for outcome prediction in traumatic brain injury
- PMID: 35915430
- PMCID: PMC9341077
- DOI: 10.1186/s12911-022-01953-z
An interpretable neural network for outcome prediction in traumatic brain injury
Abstract
Background: Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) is a common condition with potentially severe long-term complications, the prediction of which remains challenging. Machine learning (ML) methods have been used previously to help physicians predict long-term outcomes of TBI so that appropriate treatment plans can be adopted. However, many ML techniques are "black box": it is difficult for humans to understand the decisions made by the model, with post-hoc explanations only identifying isolated relevant factors rather than combinations of factors. Moreover, such models often rely on many variables, some of which might not be available at the time of hospitalization.
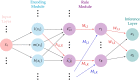
Methods: In this study, we apply an interpretable neural network model based on tropical geometry to predict unfavorable outcomes at six months from hospitalization in TBI patients, based on information available at the time of admission.
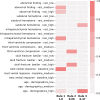
Results: The proposed method is compared to established machine learning methods-XGBoost, Random Forest, and SVM-achieving comparable performance in terms of area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC)-0.799 for the proposed method vs. 0.810 for the best black box model. Moreover, the proposed method allows for the extraction of simple, human-understandable rules that explain the model's predictions and can be used as general guidelines by clinicians to inform treatment decisions.
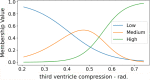
Conclusions: The classification results for the proposed model are comparable with those of traditional ML methods. However, our model is interpretable, and it allows the extraction of intelligible rules. These rules can be used to determine relevant factors in assessing TBI outcomes and can be used in situations when not all necessary factors are known to inform the full model's decision.
Keywords: Clinical decision support systems; Interpretable machine learning; Neural networks; Outcome prediction; Traumatic brain injury.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Jonathan Gryak and Kayvan Najarian are named inventors on a patent application related to the tropical geometry-based fuzzy neural network used in this work. All other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures