Complicated femoral hernia: Minimally invasive surgery management
- PMID: 35915525
- PMCID: PMC10695306
- DOI: 10.4103/jmas.jmas_119_22
Complicated femoral hernia: Minimally invasive surgery management
Abstract
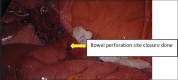
Introduction: Complicated femoral hernias can be managed by minimally invasive surgery techniques in the select group of patients. This helps reduce the morbidity of open surgery and enables faster recovery of the patient.
Concerns addressed: Delay in diagnosis can be reduced by a good clinical examination of the patient with a high index of suspicion for these patients. Imaging helps to confirm the clinical diagnosis and plan the operative intervention. In trained hands, the complicated femoral hernias can be managed by laparoscopy which enables better visualisation. Post-operative recovery is also enabled by the minimally invasive surgery done.
Conclusion: Minimally invasive laparoscopic surgery can be done in the select group of cases of complicated femoral hernia by trained surgeons.
Keywords: Complications; diagnosis; femoral hernia; minimally invasive surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
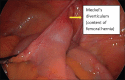
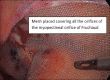
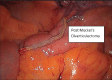
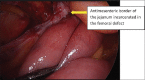

References
-
- Ogbuanya AU, Olisa FU, Ewah RL, Nweke O, Ugwu NB. Femoral hernia: Epidemiology and challenges of management in a sub-saharan African country. Asian J Med Sci. 2020;11:77–83.
-
- Smith A, Bilezikian J, Hope W, Fox S. Laparoscopic mesh repair of strangulated groin hernias requiring bowel resection. Mini Invasive Surg. 2021;5:5–9.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

