Perception and determinants of Social Networking Sites (SNS) on spreading awareness and panic during the COVID-19 pandemic in Bangladesh
- PMID: 35915626
- PMCID: PMC9330577
- DOI: 10.1016/j.hpopen.2022.100075
Perception and determinants of Social Networking Sites (SNS) on spreading awareness and panic during the COVID-19 pandemic in Bangladesh
Abstract
Introduction: The COVID-19 pandemic is an unprecedented and unique fallout worldwide and creates colossal disruption in human survival. During the pandemic, social networking sites (SNS) played a significant role in disseminating news related to the pandemic.
Methods: This research is based on primary data collected from 400 successful respondents via online Google Form. Bivariate Pearson's Chi-square and multivariate binary logistic regression analysis were performed to determine the impact of the explanatory variables on the study variables.
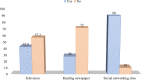
Results: This study reveals that most respondents (n = 360, 90 %) use SNS to get up-to-date news, and 72.5 % (n = 290) read health-related information. The highest number of participants (n = 386, 96.5 %) were Facebook users. Multivariate binary logistic regression reveals that "reading news on SNS" and "sharing information related to COVID-19 on social media" significantly influence the spread of awareness of COVID-19. "Unauthentic news sources" and "stop using social media to stay away from panic" also have a substantial impact on the spread of panic during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Conclusion: SNS has become an inevitable medium of information carrier nowadays. Social media users are found significantly aware of the COVID-19 pandemic. The findings of this study might assist the concerned persons in taking the necessary steps to propagate authentic news and regulate appropriate policies to prevent spreading misinformation.
Keywords: Awareness; Bangladesh; COVID-19; COVID-19, Coronavirus Disease 2019; IEDCR, Institute of Epidemiology, Disease Control and Research; Misinformation; PSTD, Post-traumatic stress disorder; Panic; SNS, Social Networking Sites; Social networking site; Spread; WHO, World Health Organization.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Impact of Social Media on Panic During the COVID-19 Pandemic in Iraqi Kurdistan: Online Questionnaire Study.J Med Internet Res. 2020 May 19;22(5):e19556. doi: 10.2196/19556. J Med Internet Res. 2020. PMID: 32369026 Free PMC article.
-
The role of social media in spreading panic among primary and secondary school students during the COVID-19 pandemic: An online questionnaire study from the Gaza Strip, Palestine.Heliyon. 2020 Dec 21;6(12):e05807. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05807. eCollection 2020 Dec. Heliyon. 2020. PMID: 33376831 Free PMC article.
-
The Negative Impact of Social Media during COVID-19 Pandemic.Trends Psychol. 2023;31(1):123-142. doi: 10.1007/s43076-022-00192-5. Epub 2022 May 16. Trends Psychol. 2023. PMID: 40477978 Free PMC article.
-
FOMO (fate of online media only) in infectious disease modeling: a review of compartmental models.Int J Dyn Control. 2023;11(2):892-899. doi: 10.1007/s40435-022-00994-6. Epub 2022 Jul 13. Int J Dyn Control. 2023. PMID: 35855912 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 pandemic hype: Losers and gainers.Indian J Psychiatry. 2020 Sep;62(Suppl 3):S420-S430. doi: 10.4103/psychiatry.IndianJPsychiatry_1060_20. Epub 2020 Sep 28. Indian J Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 33227075 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The challenges brought by the COVID-19 pandemic to health systems exposed pre-existing gaps.Health Policy Open. 2023 Dec;4:100088. doi: 10.1016/j.hpopen.2022.100088. Epub 2022 Dec 15. Health Policy Open. 2023. PMID: 36536931 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
COVID-19 Resilience and Risk Reduction Intervention in Rural Populations of Western India: Retrospective Evaluation.JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2024 Jul 29;10:e47520. doi: 10.2196/47520. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2024. PMID: 39073851 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dalili M., Dastani M. The Role of Social Media During the COVID-19 Crisis: a Narrative Review. Health Technol Assess Action. 2020;4
-
- Saud M, Mashud MI, Ida R. Usage of Social media in Pandemic: Seeking support and awareness about COVID-19 through Social Media Platforms (Preprint). 2020.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources