Tandem Friedel-Crafts-Alkylation-Enantioselective-Protonation by Artificial Enzyme Iminium Catalysis
- PMID: 35915643
- PMCID: PMC9313897
- DOI: 10.1002/cctc.202101875
Tandem Friedel-Crafts-Alkylation-Enantioselective-Protonation by Artificial Enzyme Iminium Catalysis
Abstract
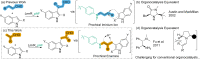
The incorporation of organocatalysts into protein scaffolds holds the promise of overcoming some of the limitations of this powerful catalytic approach. Previously, we showed that incorporation of the non-canonical amino acid para-aminophenylalanine into the non-enzymatic protein scaffold LmrR forms a proficient and enantioselective artificial enzyme (LmrR_pAF) for the Friedel-Crafts alkylation of indoles with enals. The unnatural aniline side-chain is directly involved in catalysis, operating via a well-known organocatalytic iminium-based mechanism. In this study, we show that LmrR_pAF can enantioselectively form tertiary carbon centres not only during C-C bond formation, but also by enantioselective protonation, delivering a proton to one face of a prochiral enamine intermediate. The importance of various side-chains in the pocket of LmrR is distinct from the Friedel-Crafts reaction without enantioselective protonation, and two particularly important residues were probed by exhaustive mutagenesis.
Keywords: Artificial Enzymes; Enantioselective Protonation; Friedel-Crafts Alkylations; Iminium Catalysis; Non-canonical Amino Acids.
© 2022 The Authors. ChemCatChem published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Chen K., Arnold F. H., Nat. Catal. 2020, 3, 203–213.
-
- Leveson-Gower R. B., Mayer C., Roelfes G., Nat. Rev. Chem. 2019, 3, 687–705.
-
- Sheldon R. A., Woodley J. M., Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 801–838. - PubMed
-
- Kiss G., Çelebi-Ölçüm N., Moretti R., Baker D., Houk K. N., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 5700–5725; - PubMed
- Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 5810–5836.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
