Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha Inhibitors and Cardiovascular Risk in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 35915691
- PMCID: PMC9337794
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.26430
Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha Inhibitors and Cardiovascular Risk in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that, if untreated or poorly controlled, can cause significant morbidity in terms of loss of physical function and higher mortality due to higher cardiovascular risk. The standard of care for this disease is the use of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). However, patients unable to reach low disease activity or remission and patients unable to tolerate conventional DMARDs will be switched to biologic therapy, a subset of which includes anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitors. Since tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitors (TNFi) inhibit the inflammatory cascade, they also play an essential role in dampening the progression of atherosclerosis and altering the risk of cardiovascular outcomes in RA. In this study, we assessed the risk of cardiovascular diseases, namely, congestive heart failure, nonfatal myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular disease, and coronary artery disease. We carried out the analysis by following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines and conducted a literature search utilizing the following databases: PubMed, Science Direct, and Cochrane Library. Using the search strategy, we found a total of 19 articles that fit the inclusion and exclusion criteria, in addition to passing the risk of bias assessment. This is composed of three systematic reviews with meta-analyses, three randomized control studies, four narrative reviews, and nine cohort studies. In this systematic review, it was found that treatment with TNFi causes a corresponding reduction in the risk of cardiovascular events. This review encourages further dissection into the inner workings of TNFi in reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease among patients with RA.
Keywords: cerebrovascular diseases; congestive heart failure; myocardial ischemia and infarction; reduce the risk of coronary artery disease in rheumatoid arthritis; rheumatoid arthritis; risk of cardiovascular diseases; tumor necrosis factor-alpha (tnf-α) inhibitors.
Copyright © 2022, Nair et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
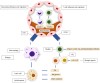
References
-
- Rheumatoid arthritis: common questions about diagnosis and management. Wasserman A. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29671563/ Am Fam Physician. 2018;97:455–462. - PubMed
-
- Specific autoantibodies precede the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis: a study of serial measurements in blood donors. Nielen MM, van Schaardenburg D, Reesink HW, et al. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50:380–386. - PubMed
-
- 2010 rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, et al. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62:2569–2581. - PubMed
-
- Risk of cardiovascular mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Aviña-Zubieta JA, Choi HK, Sadatsafavi M, Etminan M, Esdaile JM, Lacaille D. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;59:1690–1697. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
