Psychological behavior management techniques to alleviate dental fear and anxiety in 4-14-year-old children in pediatric dentistry: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 35915712
- PMCID: PMC9338387
Psychological behavior management techniques to alleviate dental fear and anxiety in 4-14-year-old children in pediatric dentistry: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
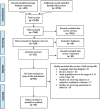
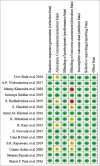
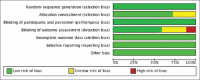
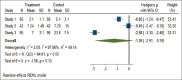
Child's uncooperative behavior can impede the efficient delivery of dental care. Therefore, in spite of exceeding availability of behavior management techniques there is a need to search for a psychological behavior management technique that effectively reduces fear and anxiety during dental treatment and instill a change in child's attitude toward the treatment and is also acceptable by the parents. The aim of our systematic review is to determine the efficacy of various psychological behavior management techniques in managing a child's behavior in pediatric dentistry by assessing the fear and anxiety levels, ease of use by the clinician, application in various operative procedures, and parental acceptance. A systematic search was conducted by two reviewers in databases PubMed, Google Scholar, Scopus, Web of Science, and Cochrane for the studies published from January 1, 2011, to December 31, 2020. Studies included were clinical studies which evaluated the efficacy of various psychological behavior management techniques by evaluating the fear and anxiety levels and the changes in behavior during dental treatment in children aged between 4 and 14 years. The studies selected were then assessed for quality with the help of predetermined criteria which categorized the studies into high, medium, and low. Through search strategy, 7147 articles were yielded. After screening through titles and abstracts, 60 nonduplicated articles were selected which were further screened for full text. At the end, 15 articles were included in systematic review and 3 articles for meta-analysis. It was concluded that all the psychological behavior management techniques aided in reduction of fear and anxiety. In noninvasive procedures, conventional psychological behavior management techniques can be effective but in invasive procedures other newer psychological behavior management techniques showed better results. The aspect of parental acceptance regarding various techniques was not discussed in any of the included studies.
Keywords: Cooperative behaviors; dental anxieties; dental fear; pedodontics.
Copyright: © 2022 Dental Research Journal.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript declare that they have no conflicts of interest, real or perceived, financial or nonfinancial in this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Parental involvement in their school-aged children's post-operative pain management in the hospital setting: a comprehensive systematic review.JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2011;9(28):1193-1225. doi: 10.11124/01938924-201109280-00001. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2011. PMID: 27820216
-
Evaluation of the Treatment Protocols in the Management of Pulpally Involved Young Permanent Teeth in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2022;15(Suppl 1):S103-S113. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-2218. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2022. PMID: 35645501 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beyond the black stump: rapid reviews of health research issues affecting regional, rural and remote Australia.Med J Aust. 2020 Dec;213 Suppl 11:S3-S32.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50881. Med J Aust. 2020. PMID: 33314144
-
Use of distraction techniques for the management of anxiety and fear in paediatric dental practice: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials.Int J Paediatr Dent. 2019 Sep;29(5):650-668. doi: 10.1111/ipd.12499. Epub 2019 Apr 25. Int J Paediatr Dent. 2019. PMID: 30908775
-
Evidence of pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions for the management of dental fear in paediatric dentistry: a systematic review protocol.BMJ Open. 2017 Aug 18;7(8):e016043. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-016043. BMJ Open. 2017. PMID: 28821522 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Sensory Processing Disorder in Children-Description of the Phenomenon and Practical Procedures.J Clin Med. 2025 Jun 10;14(12):4105. doi: 10.3390/jcm14124105. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40565851 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative evaluation of efficacy and safety of nitrous oxide and midazolam for conscious sedation in pediatric dental patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Dent Anesth Pain Med. 2025 Jun;25(3):161-182. doi: 10.17245/jdapm.2025.25.3.161. Epub 2025 May 30. J Dent Anesth Pain Med. 2025. PMID: 40521429 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Observational Study on Progressive Muscle Relaxation and Breathing Control for Reducing Dental Anxiety in Children.Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 May 10;61(5):876. doi: 10.3390/medicina61050876. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 40428834 Free PMC article.
-
AI-Driven Innovations in Pediatric Dentistry: Enhancing Care and Improving Outcome.Cureus. 2024 Sep 12;16(9):e69250. doi: 10.7759/cureus.69250. eCollection 2024 Sep. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39398765 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Evaluation of Acupressure, Aromatherapy, and Stress Ball Efficacy in Reduction of Anxiety Levels in Children during Prophylactic and Restorative Procedures.Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2025 Feb;18(2):210-214. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-3070. Epub 2025 Mar 20. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2025. PMID: 40417433 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Paryab M, Hosseinbor M. Dental anxiety and behavioral problems: A study of prevalence and related factors among a group of Iranian children aged 6-12. J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent. 2013;31:82–6. - PubMed
-
- Townsend JA, Wells MH. Behavior guidance of the pediatric dental patient. Pedia Dent. 2019:352–70.
-
- Higgins JP, Green S. Wiley Online Library. The Cochrane Collaboration; 2008. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Review.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
