Gene Identification and Potential Drug Therapy for Drug-Resistant Melanoma with Bioinformatics and Deep Learning Technology
- PMID: 35915735
- PMCID: PMC9338845
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/2461055
Gene Identification and Potential Drug Therapy for Drug-Resistant Melanoma with Bioinformatics and Deep Learning Technology
Abstract
Background: Melanomas are skin malignant tumors that arise from melanocytes which are primarily treated with surgery, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, radiation therapy, etc. Targeted therapy is a promising approach to treating advanced melanomas, but resistance always occurs. This study is aimed at identifying the potential target genes and candidate drugs for drug-resistant melanoma effectively with computational methods.
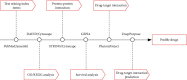
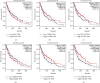
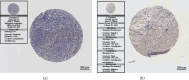
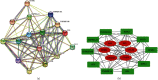
Methods: Identification of genes associated with drug-resistant melanomas was conducted using the text mining tool pubmed2ensembl. Further gene screening was carried out by GO and KEGG pathway enrichment analyses. The PPI network was constructed using STRING database and Cytoscape. GEPIA was used to perform the survival analysis and conduct the Kaplan-Meier curve. Drugs targeted at these genes were selected in Pharmaprojects. The binding affinity scores of drug-target interactions were predicted by DeepPurpose.
Results: A total of 433 genes were found associated with drug-resistant melanomas by text mining. The most statistically differential functional enriched pathways of GO and KEGG analyses contained 348 genes, and 27 hub genes were further screened out by MCODE in Cytoscape. Six genes were identified with statistical differences after survival analysis and literature review. 16 candidate drugs targeted at hub genes were found by Pharmaprojects under our restrictions. Finally, 11 ERBB2-targeted drugs with top affinity scores were predicted by DeepPurpose, including 10 ERBB2 kinase inhibitors and 1 antibody-drug conjugate.
Conclusion: Text mining and bioinformatics are valuable methods for gene identification in drug discovery. DeepPurpose is an efficient and operative deep learning tool for predicting the DTI and selecting the candidate drugs.
Copyright © 2022 Muge Liu and Yingbin Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Identification of Potential Drug Therapy for Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans with Bioinformatics and Deep Learning Technology.Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2022;18(5):393-405. doi: 10.2174/1573409918666220816112206. Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2022. PMID: 35975851 Review.
-
Screening and identification of potential biomarkers and therapeutic drugs in melanoma via integrated bioinformatics analysis.Invest New Drugs. 2021 Aug;39(4):928-948. doi: 10.1007/s10637-021-01072-y. Epub 2021 Jan 26. Invest New Drugs. 2021. PMID: 33501609
-
Identification of core genes and pathways between geriatric multimorbidity and renal insufficiency: potential therapeutic agents discovered using bioinformatics analysis.BMC Med Genomics. 2022 Oct 8;15(1):212. doi: 10.1186/s12920-022-01370-1. BMC Med Genomics. 2022. PMID: 36209090 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of key genes and pathways in scleral extracellular matrix remodeling in glaucoma: Potential therapeutic agents discovered using bioinformatics analysis.Int J Med Sci. 2021 Feb 4;18(7):1554-1565. doi: 10.7150/ijms.52846. eCollection 2021. Int J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33746571 Free PMC article.
-
Screening and Identification of Key Biomarkers in Melanoma: Evidence from Bioinformatic Analyses.J Comput Biol. 2021 Mar;28(3):317-329. doi: 10.1089/cmb.2019.0400. Epub 2020 Sep 25. J Comput Biol. 2021. PMID: 32985909
Cited by
-
Luteolin and triptolide: Potential therapeutic compounds for post-stroke depression via protein STAT.Heliyon. 2023 Aug 3;9(8):e18622. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e18622. eCollection 2023 Aug. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37600392 Free PMC article.
-
Antitumor activity of anlotinib in malignant melanoma: modulation of angiogenesis and vasculogenic mimicry.Arch Dermatol Res. 2024 Jul 3;316(7):447. doi: 10.1007/s00403-024-03020-1. Arch Dermatol Res. 2024. PMID: 38958761
-
Innovative applications of artificial intelligence in zoonotic disease management.Sci One Health. 2023 Nov 3;2:100045. doi: 10.1016/j.soh.2023.100045. eCollection 2023. Sci One Health. 2023. PMID: 39077042 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

