Effects of bone morphogenetic protein 4 on TGF- β 1-induced cell proliferation, apoptosis, activation and differentiation in mouse lung fibroblasts via ERK/p38 MAPK signaling pathway
- PMID: 35915750
- PMCID: PMC9338752
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.13775
Effects of bone morphogenetic protein 4 on TGF- β 1-induced cell proliferation, apoptosis, activation and differentiation in mouse lung fibroblasts via ERK/p38 MAPK signaling pathway
Abstract
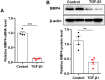
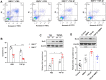
Fibroblasts, in particular myofibroblasts, are the critical effector cells in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), a deadly lung disease characterized by abnormal lung remodeling and the formation of "fibroblastic foci". Aberrant activation of TGF-β1 is frequently encountered and promotes fibroblast proliferation, activation, and differentiation in pulmonary fibrosis. Hence, the inhibition of TGF-β1-induced lung fibroblast activation holds promise as a therapeutic strategy for IPF. The present study aimed to investigate the potential effect and underlying mechanisms of bone morphogenetic protein 4 (BMP4) on TGF-β1-induced proliferation, apoptosis, activation and myofibroblast differentiation of adult lung fibroblasts. Here, we demonstrated that BMP4 expression was significantly decreased in TGF-β1-stimulated mouse primary lung fibroblasts (PLFs). BMP4 inhibited proliferation and apoptosis resistance of TGF-β1-stimulated mouse PLFs. BMP4 suppressed TGF-β1-induced fibroblast activation and differentiation in mouse PLFs. We also found that BMP4 inhibited TGF-β1-induced ERK and p38 MAPK phosphorylation. Our findings indicate that BMP4 exerts its anti-fibrotic effects by regulating fibroblast proliferation, apoptosis, activation and differentiation via the inhibition of the ERK/p38 MAPK signaling pathway, and thus has a potential for the treatment of pulmonary fibrosis.
Keywords: Activation; Apoptosis; BMP4; Fibroblasts; Pulmonary fibrosis; TGF-β1.
©2022 Cai et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Andrographolide ameliorates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by suppressing cell proliferation and myofibroblast differentiation of fibroblasts via the TGF-β1-mediated Smad-dependent and -independent pathways.Toxicol Lett. 2020 Mar 15;321:103-113. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2019.11.003. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Toxicol Lett. 2020. PMID: 31706003
-
Follistatin-Like 1 Promotes Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis through the Transforming Growth Factor Beta 1/Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling Pathway.Chin Med J (Engl). 2018 Aug 20;131(16):1917-1925. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.238151. Chin Med J (Engl). 2018. PMID: 30082522 Free PMC article.
-
Bone morphogenetic protein 4 inhibits pulmonary fibrosis by modulating cellular senescence and mitophagy in lung fibroblasts.Eur Respir J. 2022 Dec 15;60(6):2102307. doi: 10.1183/13993003.02307-2021. Print 2022 Dec. Eur Respir J. 2022. PMID: 35777761 Free PMC article.
-
Revisiting the role of MicroRNAs in the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Oct 16;12:1470875. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1470875. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39479511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiac Fibroblast p38 MAPK: A Critical Regulator of Myocardial Remodeling.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2019 Aug 7;6(3):27. doi: 10.3390/jcdd6030027. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2019. PMID: 31394846 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Crosstalk of ubiquitin system and non-coding RNA in fibrosis.Int J Biol Sci. 2024 Jul 8;20(10):3802-3822. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.93644. eCollection 2024. Int J Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39113708 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Noncoding RNAs: Master Regulator of Fibroblast to Myofibroblast Transition in Fibrosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 16;24(2):1801. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021801. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36675315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Umbilical cord blood-derived exosomes attenuate dopaminergic neuron damage of Parkinson's disease mouse model.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Sep 14;22(1):567. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02773-1. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 39277761 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burgess HA, Daugherty LE, Thatcher TH, Lakatos HF, Ray DM, Redonnet M, Phipps RP, Sime PJ. PPARgamma agonists inhibit TGF-beta induced pulmonary myofibroblast differentiation and collagen production: implications for therapy of lung fibrosis. The American Journal of Physiology-Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology. 2005;288:L1146–L1153. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00383.2004. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen YL, Zhang X, Bai J, Gai L, Ye XL, Zhang L, Xu Q, Zhang YX, Xu L, Li HP, Ding X. Sorafenib ameliorates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis: potential roles in the inhibition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and fibroblast activation. Cell Death & Disease. 2013;4:e665. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.154. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

