Application of edge computing combined with deep learning model in the dynamic evolution of network public opinion in emergencies
- PMID: 35915780
- PMCID: PMC9330939
- DOI: 10.1007/s11227-022-04733-8
Application of edge computing combined with deep learning model in the dynamic evolution of network public opinion in emergencies
Abstract
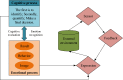
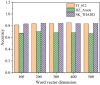
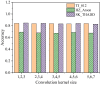
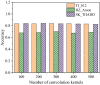
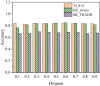
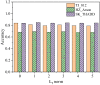
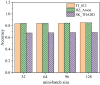
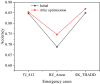
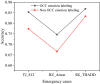
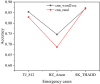
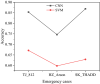
The aim is to clarify the evolution mechanism of Network Public Opinion (NPO) in public emergencies. This work makes up for the insufficient semantic understanding in NPO-oriented emotion analysis and tries to maintain social harmony and stability. The combination of the Edge Computing (EC) and Deep Learning (DL) model is applied to the NPO-oriented Emotion Recognition Model (ERM). Firstly, the NPO on public emergencies is introduced. Secondly, three types of NPO emergencies are selected as research cases. An emotional rule system is established based on the One-Class Classification (OCC) model as emotional standards. The word embedding representation method represents the preprocessed Weibo text data. Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) is used as the classifier. The NPO-oriented ERM is implemented on CNN and verified through comparative experiments after the CNN's hyperparameters are adjusted. The research results show that the text annotation of the NPO based on OCC emotion rules can obtain better recognition performance. Additionally, the recognition effect of the improved CNN is significantly higher than the Support Vector Machine (SVM) in traditional Machine Learning (ML). This work realizes the technological innovation of automatic emotion recognition of NPO groups and provides a basis for the relevant government agencies to handle the NPO in public emergencies scientifically.
Keywords: CNN; Deep learning; Emotion recognition; Network public opinion; Public emergency.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature 2022, Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestAll Authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A CNN-Based Framework for Predicting Public Emotion and Multi-Level Behaviors Based on Network Public Opinion.Front Psychol. 2022 Jun 23;13:909439. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.909439. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 35814112 Free PMC article.
-
Emotion recognition of social media users based on deep learning.PeerJ Comput Sci. 2023 Jun 14;9:e1414. doi: 10.7717/peerj-cs.1414. eCollection 2023. PeerJ Comput Sci. 2023. PMID: 37346659 Free PMC article.
-
Legal Early Warning of Public Crisis in Network Public Opinion Events Based on Emotional Tendency.J Environ Public Health. 2022 Aug 23;2022:6367295. doi: 10.1155/2022/6367295. eCollection 2022. J Environ Public Health. 2022. Retraction in: J Environ Public Health. 2023 Jun 28;2023:9767019. doi: 10.1155/2023/9767019. PMID: 36052349 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
A Simplified Framework for the Detection of Intracranial Hemorrhage in CT Brain Images Using Deep Learning.Curr Med Imaging. 2021;17(10):1226-1236. doi: 10.2174/1573405617666210218100641. Curr Med Imaging. 2021. PMID: 33602101 Review.
-
Mini-review: Recent advances in post-translational modification site prediction based on deep learning.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022 Jun 30;20:3522-3532. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.06.045. eCollection 2022. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 35860402 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A bigura-based real time sentiment analysis of new media.PeerJ Comput Sci. 2024 Jun 28;10:e2069. doi: 10.7717/peerj-cs.2069. eCollection 2024. PeerJ Comput Sci. 2024. PMID: 39669474 Free PMC article.
-
Distributed opinion competition scheme with gradient-based neural network in social networks.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 28;14(1):30883. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-81857-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39730650 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lin L, Jiang A, Zheng Y, et al. New media platform's understanding of Chinese social workers' anti-epidemic actions: an analysis of network public opinion based on COVID-19. Social Work in Public Health, 2021: 1–16. - PubMed
-
- Rim H, Lee Y, Yoo S. Polarized public opinion responding to corporate social advocacy: social network analysis of boycotters and advocators. Public Relations Review. 2020;46(2):101869. doi: 10.1016/j.pubrev.2019.101869. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
