Influence of Nutritional Support Program on Gastrointestinal Function, Complication Rate, and Prognosis in Elderly Sufferers with CI
- PMID: 35915802
- PMCID: PMC9338853
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/3198272
Influence of Nutritional Support Program on Gastrointestinal Function, Complication Rate, and Prognosis in Elderly Sufferers with CI
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Influence of Nutritional Support Program on Gastrointestinal Function, Complication Rate, and Prognosis in Elderly Sufferers with CI.Biomed Res Int. 2023 Aug 2;2023:9809457. doi: 10.1155/2023/9809457. eCollection 2023. Biomed Res Int. 2023. PMID: 37564140 Free PMC article.
Abstract
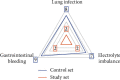
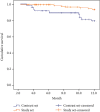
To explore the effect of nutritional support program on gastrointestinal function, complication rate, and prognosis in elderly patients with cerebral infarction (CI), 200 elderly patients with CI from January 2020 to January 2021 are investigated in this study. The patients were randomly divided into a study set and a control group, with 100 cases in each set. All sets were given routine treatment, the control set was given parenteral nutrition support on a routine basis, and the study set was given enteral nutrition support on a routine basis. First, the clinical efficacy of the two sets after treatment was compared. Next, the constipation symptom score was adopted to compare the intestinal function of the two sets of patients before and after one month of treatment. The nutritional indicators, including serum albumin (ALB) and serum total protein (TP) levels, were compared between the two sets of patients before and after one month of treatment. Furthermore, the complications of the two sets of patients and the prognosis of the two groups of patients are analyzed. For elderly CI patients, enteral nutrition support therapy can significantly improve the clinical treatment effect, the gastrointestinal function, and nutritional index level. Also, it can reduce the incidence of complications and enhance the prognosis, survival rate, and quality of life.
Copyright © 2022 Huijuan Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Zhu X. L., Sun F. H. Application effect of early enteral nutrition nursing intervention on sufferers after massive cerebral infarction decompression. Clinical Research and Practice . 2019;7(16):369–372.
-
- Xian H. Effect of early enteral nutrition nursing intervention on the prognosis of sufferers after extensive cerebral infarction decompression. Chinese Journal of Practical Nervous Diseases . 2019;22(20):2264–2269.
-
- Wang L. F., Tang X. H., Zhang X. X. Influencing factors of misinhalation in sufferers with severe cerebral infarction undergoing enteral nutrition support and nursing strategies. Hainan Medical Journal . 2019;30(16):2167–2169.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous