Staphylococcal Cassette Chromosome mec Typing and Multilocus Variable Number Tandem Repeat Analysis of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Clinical Isolates with Vancomycin Creep Phenomenon
- PMID: 35915809
- PMCID: PMC9338391
- DOI: 10.2147/IDR.S368912
Staphylococcal Cassette Chromosome mec Typing and Multilocus Variable Number Tandem Repeat Analysis of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Clinical Isolates with Vancomycin Creep Phenomenon
Abstract
Background: The association of treatment failure and mortality with vancomycin minimum inhibitory concentration creep (MIC) is a matter of serious concern in patients with severe methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infections. The purpose of the study was to identify and characterize staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec (SCCmec) and clonal types of MRSA strains, exhibiting the vancomycin MIC creep phenomenon.
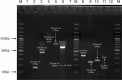
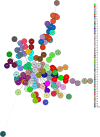
Methods: A total of 3305 S. aureus strains were isolated from various clinical samples of Lahore General Hospital, Lahore, Pakistan. MRSA strains were identified by cefoxitin resistant (≤21mm) followed by mecA and mecC gene genotyping. Vancomycin MIC creep was determined by E-test. Isolates having MIC values >1.5 µg/mL were further subjected for SCCmec typing (I-V and XI) and multiple-locus variable number tandem repeat analysis (MLVA) by amplification of spa, sspA, clfA, clfB, and sdrCDE genes. A dendrogram was created based on the similarity index using bioneumerics software.
Results: About 13.3% (440/3305) isolates were MRSA with 99.3% (437/440) and 0.7% (3/440) carried mecA and mecC genes, respectively. In 120 MRSA isolates, the MIC of vancomycin was >1.5µg/mL. In MRSA isolates with high vancomycin MIC (>1.5µg/mL), the most common SCCmec type was SCCmec III (38.3%), followed by SCCmec IVa (15.8%), SCCmec IIIa (13.3%,), SCCmec IVc (7.5%), SCCmec IVe (5.8%), SCCmec IVd (5.8%), SCCmec IVb (4.2%), SCCmec II (2.5%), SCCmec V (1.7%), SCCmec I (1.7%) and SCCmec XI (1.7%). MLVA revealed 60 genotypic groups of MRSA isolates having a 92% similarity index.
Conclusion: SCCmec III was the most common type in genetically related MRSA isolates showing vancomycin MIC creep. The presence of SCCmec XI may further add burden to infection control measures.
Keywords: methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus; multilocus variable number tandem repeat analysis; staphylococcal chromosomal cassette.
© 2022 Arshad et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or nonfinancial interest to disclose in this work.
Figures



References
-
- Kaleem F, Usman J, Khalid A, Hassan A, Omair M. Comparison of in vitro efficacy of linezolid and vancomycin by determining their minimum inhibitory concentrations against methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). J Pak Med Assoc. 2011;61(4):356–359. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

