Selenoprotein I deficiency in T cells promotes differentiation into tolerant phenotypes while decreasing Th17 pathology
- PMID: 35916034
- PMCID: PMC9701159
- DOI: 10.1002/JLB.1A0122-080R
Selenoprotein I deficiency in T cells promotes differentiation into tolerant phenotypes while decreasing Th17 pathology
Abstract
Selenoprotein I (SELENOI) is an ethanolamine phospholipid transferase contributing to cellular metabolism and the synthesis of glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchors. SELENOI knockout (KO) in T cells has been shown to impair metabolic reprogramming during T cell activation and reduce GPI-anchored Thy-1 levels, which are both crucial for Th17 differentiation. This suggests SELENOI may be important for Th17 differentiation, and we found that SELENOI was indeed up-regulated early during the activation of naïve CD4+ T cells in Th17 conditions. SELENOI KO reduced RORγt mRNA levels by decreasing SOX5 and STAT3 binding to promoter and enhancer regions in the RORC gene encoding this master regulator of Th17 cell differentiation. Differentiation of naïve CD4+ T cells into inflammatory versus tolerogenic Th cell subsets was analyzed and results showed that SELENOI deficiency skewed differentiation away from pathogenic Th17 cells (RORγt+ and IL-17A+ ) while promoting tolerogenic phenotypes (Foxp3+ and IL-10+ ). Wild-type and T cell-specific SELENOI KO mice were subjected to experimental autoimmune encephalitis (EAE), with KO mice exhibiting diminished clinical symptoms, reduced CNS pathology and decreased T cell infiltration. Flow cytometry showed that SELENOI T cell KO mice exhibited lower CD4+ RORγt+ and CD4+ IL-17A+ T cells and higher CD4+ CD25+ FoxP3+ T cells in CNS tissues of mice subjected to EAE. Thus, the metabolic enzyme SELENOI is up-regulated to promote RORγt transcription that drives Th17 differentiation, and SELENOI deficiency shifts differentiation toward tolerogenic phenotypes while protecting against pathogenic Th17 responses.
Keywords: autoimmunity; ethanolamine phospholipid transferase; inflammation; metabolism; phosphatidylethanolamine.
©2022 Society for Leukocyte Biology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-Interest Disclosure
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures

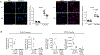


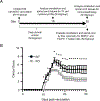
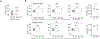
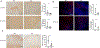
References
-
- Chisolm DA and Weinmann AS (2018) Connections Between Metabolism and Epigenetics in Programming Cellular Differentiation. Annu Rev Immunol 36, 221–246. - PubMed
-
- Harrington LE, Hatton RD, Mangan PR, Turner H, Murphy TL, Murphy KM, Weaver CT (2005) Interleukin 17-producing CD4+ effector T cells develop via a lineage distinct from the T helper type 1 and 2 lineages. Nat Immunol 6, 1123–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

