IL-22 and Lactobacillus delbrueckii mitigate alcohol-induced exacerbation of DSS-induced colitis
- PMID: 35916052
- PMCID: PMC9701151
- DOI: 10.1002/JLB.4A0122-068R
IL-22 and Lactobacillus delbrueckii mitigate alcohol-induced exacerbation of DSS-induced colitis
Abstract
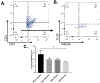
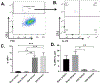
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is characterized by cycles of active disease flare and inactive disease remission. During UC remission, IL-22 is up-regulated, acting as a hallmark of entrance into UC remission. Recently, we found that in our mouse model of binge alcohol and dextran sodium sulfate (DSS)-induced colitis, alcohol increases severity of UC pathology. In this study, we assessed not only whether alcohol influenced IL-22 expression and thereby perpetuates UC, but also whether recombinant IL-22 (rIL-22) or treatment with a probiotic could alleviate exacerbated symptoms of UC. Levels of large intestine IL-22 were significantly decreased ∼6.9-fold in DSS ethanol compared with DSS vehicle. Examination of lamina propria (LP) cells in the large intestine revealed IL-22+ γδ T cells in DSS vehicle-treated mice were significantly increased, while IL-22+ γδ T cells in DSS ethanol mice were unable to mount this IL-22 response. We administered rIL-22 and found it restored weight loss of DSS ethanol-treated mice. Colonic shortening and increased Enterobacteriaceae were also attenuated. Administration of Lactobacillus delbrueckii attenuated weight loss (p < 0.01), colon length (p < 0.001), mitigated increases in Enterobacteriaceae, increased levels of IL-22, and increased levels of p-STAT3 back to that of DSS vehicle group in DSS ethanol mice. In contrast, sole administration of L. delbrueckii supernatant was not sufficient to reduce UC exacerbation following alcohol. Our findings suggest L. delbrueckii contributes to repair mechanisms by increasing levels of IL-22, resulting in phosphorylation of STAT3, thus attenuating the alcohol-induced increases in intestinal damage after colitis.
Keywords: STAT3; Ulcerative colitis; ethanol; immune cells; inflammation; probiotics.
©2022 Society for Leukocyte Biology.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures:
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures




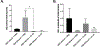
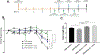
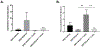
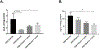


Similar articles
-
Sustained ameliorative effect of Lactobacillus acidophilus LA85 on dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice.J Food Sci. 2023 Sep;88(9):3893-3904. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.16723. Epub 2023 Aug 7. J Food Sci. 2023. PMID: 37548631
-
Different Effects of Three Selected Lactobacillus Strains in Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis in BALB/c Mice.PLoS One. 2016 Feb 3;11(2):e0148241. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148241. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26840426 Free PMC article.
-
Alcohol decreases intestinal ratio of Lactobacillus to Enterobacteriaceae and induces hepatic immune tolerance in a murine model of DSS-colitis.Gut Microbes. 2020 Nov 9;12(1):1-16. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2020.1838236. Gut Microbes. 2020. PMID: 33180663 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of Lactobacillus plantarum YS3 on dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in C57BL/6J mice.J Food Biochem. 2021 Feb;45(2):e13632. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.13632. Epub 2021 Feb 1. J Food Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33527475
-
Preventive Effect of Lactobacillus acidophilus XY27 on DSS-Induced Ulcerative Colitis in Mice.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020 Dec 22;14:5645-5657. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S284422. eCollection 2020. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020. PMID: 33376308 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Adding Fat to the Fire: Does Lipidated IL-22 Promote Mucosal Healing in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease Treated with Immunomodulators?Dig Dis Sci. 2025 Jun 23. doi: 10.1007/s10620-025-09169-7. Online ahead of print. Dig Dis Sci. 2025. PMID: 40549241 No abstract available.
-
Ethanol-induced changes to the gut microbiome compromise the intestinal homeostasis: a review.Gut Microbes. 2024 Jan-Dec;16(1):2393272. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2024.2393272. Epub 2024 Sep 3. Gut Microbes. 2024. PMID: 39224006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Probiotics on Gastrointestinal Health Through the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Pathway: A Systematic Review.Foods. 2024 Oct 30;13(21):3479. doi: 10.3390/foods13213479. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39517263 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lactobacillus helveticus attenuates alcoholic liver injury via regulation of gut microecology in mice.Microb Biotechnol. 2024 Oct;17(10):e70016. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.70016. Microb Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39431804 Free PMC article.
-
Probiotics for the treatment of ulcerative colitis: a review of experimental research from 2018 to 2022.Front Microbiol. 2023 Jul 6;14:1211271. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1211271. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37485519 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Crohn’s and colitis foundation of america. http://www.ccfa.org/resources/facts-about-inflammatory.html. Updated May, 2011March, 2016.
-
- Sartor RB. Microbial influences in inflammatory bowel diseases. Gastroenterology. 2008;134(2):577–594. - PubMed
-
- Neurath MF, Travis SP. Mucosal healing in inflammatory bowel diseases: A systematic review. Gut. 2012;61(11):1619–1635. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

