Integrated analyses of growth differentiation factor-15 concentration and cardiometabolic diseases in humans
- PMID: 35916366
- PMCID: PMC9391041
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.76272
Integrated analyses of growth differentiation factor-15 concentration and cardiometabolic diseases in humans
Abstract
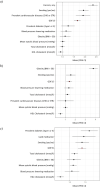
Growth differentiation factor-15 (GDF15) is a stress response cytokine that is elevated in several cardiometabolic diseases and has attracted interest as a potential therapeutic target. To further explore the association of GDF15 with human disease, we conducted a broad study into the phenotypic and genetic correlates of GDF15 concentration in up to 14,099 individuals. Assessment of 772 traits across 6610 participants in FINRISK identified associations of GDF15 concentration with a range of phenotypes including all-cause mortality, cardiometabolic disease, respiratory diseases and psychiatric disorders, as well as inflammatory markers. A meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies (GWAS) of GDF15 concentration across three different assay platforms (n=14,099) confirmed significant heterogeneity due to a common missense variant (rs1058587; p.H202D) in GDF15, potentially due to epitope-binding artefacts. After conditioning on rs1058587, statistical fine mapping identified four independent putative causal signals at the locus. Mendelian randomisation (MR) analysis found evidence of a causal relationship between GDF15 concentration and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) but not body mass index (BMI). Using reverse MR, we identified a potential causal association of BMI on GDF15 (IVW pFDR = 0.0040). Taken together, our data derived from human population cohorts do not support a role for moderately elevated GDF15 concentrations as a causal factor in human cardiometabolic disease but support its role as a biomarker of metabolic stress.
Keywords: BMI; GDF15; Mendelian randomisation; causality; epidemiology; genetics; genomics; global health; human; obesity.
© 2022, Lemmelä, Wigmore et al.
Conflict of interest statement
SL, CB, AH, TK, KW, SB, TZ, JP, AP, MD, MK No competing interests declared, EW, MF, RM, DP are employees of AstraZeneca, RO is currently an employee of GlaxoSmithKline (although was not when this work was carried out), VS has received honoraria from Novo Nordisk and Sanofi for consulting. He also has ongoing research collaboration with Bayer Ltd (all outside this work), AB reports grants outside of this work from Biogen, BioMarin, Bioverativ, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer and Sanofi and personal fees from Novartis, AM is an employee of AstraZeneca and currently an employee of GlaxoSmithKline (although not an employee of GlaxoSmithKline when this work was carried out)
Figures


References
-
- Akbari P, Gilani A, Sosina O, Kosmicki JA, Khrimian L, Fang Y-Y, Persaud T, Garcia V, Sun D, Li A, Mbatchou J, Locke AE, Benner C, Verweij N, Lin N, Hossain S, Agostinucci K, Pascale JV, Dirice E, Dunn M, Kraus WE, Shah SH, Chen Y-DI, Rotter JI, Rader DJ, Melander O, Still CD, Mirshahi T, Carey DJ, Berumen-Campos J, Kuri-Morales P, Alegre-Díaz J, Torres JM, Emberson JR, Collins R, Balasubramanian S, Hawes A, Jones M, Zambrowicz B, Murphy AJ, Paulding C, Coppola G, Overton JD, Reid JG, Shuldiner AR, Cantor M, Kang HM, Abecasis GR, Karalis K, Economides AN, Marchini J, Yancopoulos GD, Sleeman MW, Altarejos J, Della Gatta G, Tapia-Conyer R, Schwartzman ML, Baras A, Ferreira MAR, Lotta LA, Regeneron Genetics Center. DiscovEHR Collaboration Sequencing of 640,000 exomes identifies GPR75 variants associated with protection from obesity. Science. 2021;373:eabf8683. doi: 10.1126/science.abf8683. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Astle WJ, Elding H, Jiang T, Allen D, Ruklisa D, Mann AL, Mead D, Bouman H, Riveros-Mckay F, Kostadima MA, Lambourne JJ, Sivapalaratnam S, Downes K, Kundu K, Bomba L, Berentsen K, Bradley JR, Daugherty LC, Delaneau O, Freson K, Garner SF, Grassi L, Guerrero J, Haimel M, Janssen-Megens EM, Kaan A, Kamat M, Kim B, Mandoli A, Marchini J, Martens JHA, Meacham S, Megy K, O’Connell J, Petersen R, Sharifi N, Sheard SM, Staley JR, Tuna S, van der Ent M, Walter K, Wang SY, Wheeler E, Wilder SP, Iotchkova V, Moore C, Sambrook J, Stunnenberg HG, Di Angelantonio E, Kaptoge S, Kuijpers TW, Carrillo-de-Santa-Pau E, Juan D, Rico D, Valencia A, Chen L, Ge B, Vasquez L, Kwan T, Garrido-Martín D, Watt S, Yang Y, Guigo R, Beck S, Paul DS, Pastinen T, Bujold D, Bourque G, Frontini M, Danesh J, Roberts DJ, Ouwehand WH, Butterworth AS, Soranzo N. The allelic landscape of human blood cell trait variation and links to common complex disease. Cell. 2016;167:1415–1429. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.10.042. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Au Yeung SL, Luo S, Schooling CM. The impact of GDF-15, a biomarker for metformin, on the risk of coronary artery disease, breast and colorectal cancer, and type 2 diabetes and metabolic traits: a Mendelian randomisation study. Diabetologia. 2019;62:1638–1646. doi: 10.1007/s00125-019-4913-2. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

